Cryptocurrency: Full Report

From the inception to the Maturation of Crypto Markets
In January 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first Bitcoin block 1Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Retrieved from https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf, known as the Genesis Block, marking the inception of the Bitcoin network. This milestone not only launched a new era of digital currency but also catalyzed significant changes across the internet and the crypto market. Over the years, the sector has experienced dramatic fluctuations, characterized by significant market gains and losses, which have shaped its volatile history.
Initially valued at less than a penny, Bitcoin’s value soared to a historic high of over $73,000, in March 2024 2Crypto Adventure. (2024, May 22). Bitcoin seen breaching $73,000 as ‘bull run’ looms, analyst says. Crypto Adventure. Retrieved from https://cryptoadventure.com/bitcoin-seen-breaching-73000-as-bull-run-looms-analyst-says/, underscoring its potential as a lucrative yet unpredictable investment. This meteoric rise highlighted the enormous economic possibilities of cryptocurrencies and attracted a broad spectrum of investors looking to capitalize on these digital assets.
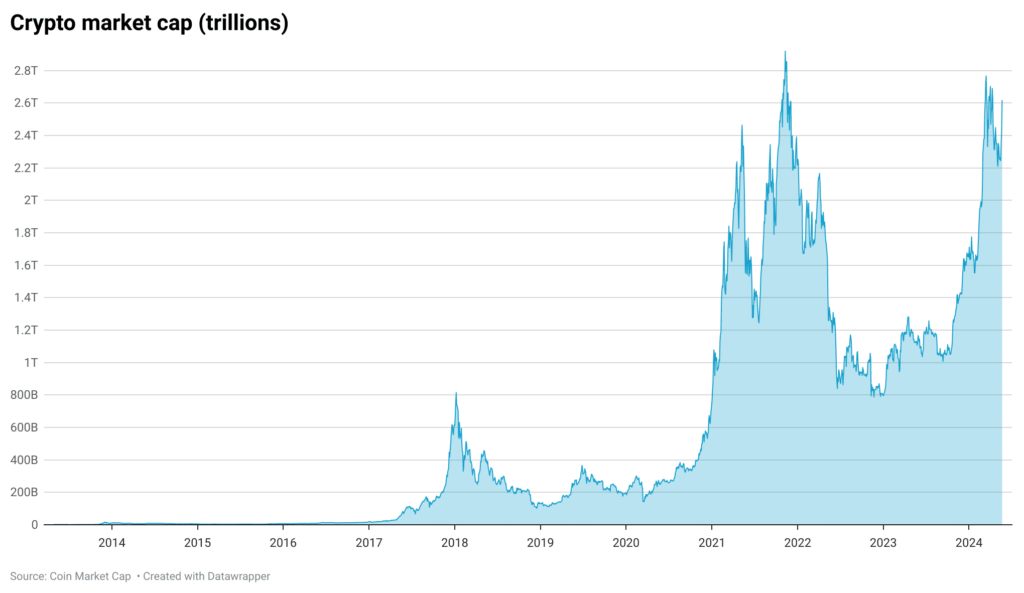
Currently, the total value of all cryptocurrencies stands at approximately $2.33 trillion, having reached all times high, $2.8 trillion, in November 2021 (chart below), with Bitcoin alone accounting for about $1.2 trillion of this market as of May 2024, according to CoinMarketCap.com. Global payments revenue is also projected to exceed $3 trillion by 2026, as reported by a McKinsey study3McKinsey & Company. (2022). The 2022 McKinsey Global Payments Report. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/financial%20services/our%20insights/the%202022%20mckinsey%20global%20payments%20report/the-2022-mckinsey-global-payments-report.pdf, indicating a rapidly expanding scope for digital financial transactions.
However, as the crypto market evolved, it became mired in controversies, including scandals related to the lack of intrinsic value4Kerr, D. S., Loveland, K. A., Smith, K. T., & Smith, L. M. (2023). Cryptocurrency risks, fraud cases, and financial performance. Risks, 11(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks11030051. and criminal activities such as money laundering and terrorism financing5Europol. (2023). Europol spotlight: Cryptocurrencies – Tracing the evolution of criminal finances. Retrieved from https://www.europol.europa.eu/cms/sites/default/files/documents/Europol%20Spotlight%20-%20Cryptocurrencies%20-%20Tracing%20the%20evolution%20of%20criminal%20finances.pdf. These challenges have become a significant part of the narrative surrounding crypto assets, reflecting the complexities and risks of integrating these new forms of currency into the global financial system.
Despite these challenges, or perhaps because of the increased attention they have garnered, interest in cryptocurrencies has skyrocketed. What began as a niche asset class, primarily of interest to tech enthusiasts and early adopters, has rapidly evolved into a crucial element of the global financial landscape. Cryptocurrencies are now fundamentally altering the way we perceive, use, and engage with money.
This transformation is reflected in the numbers: by 2024, approximately 562 million people worldwide own some form of digital currency, a dramatic increase from 420 million in 2023. This means that around 6.8% of the global population is now involved in the crypto market, underscoring the growing integration of digital currencies into mainstream finance.
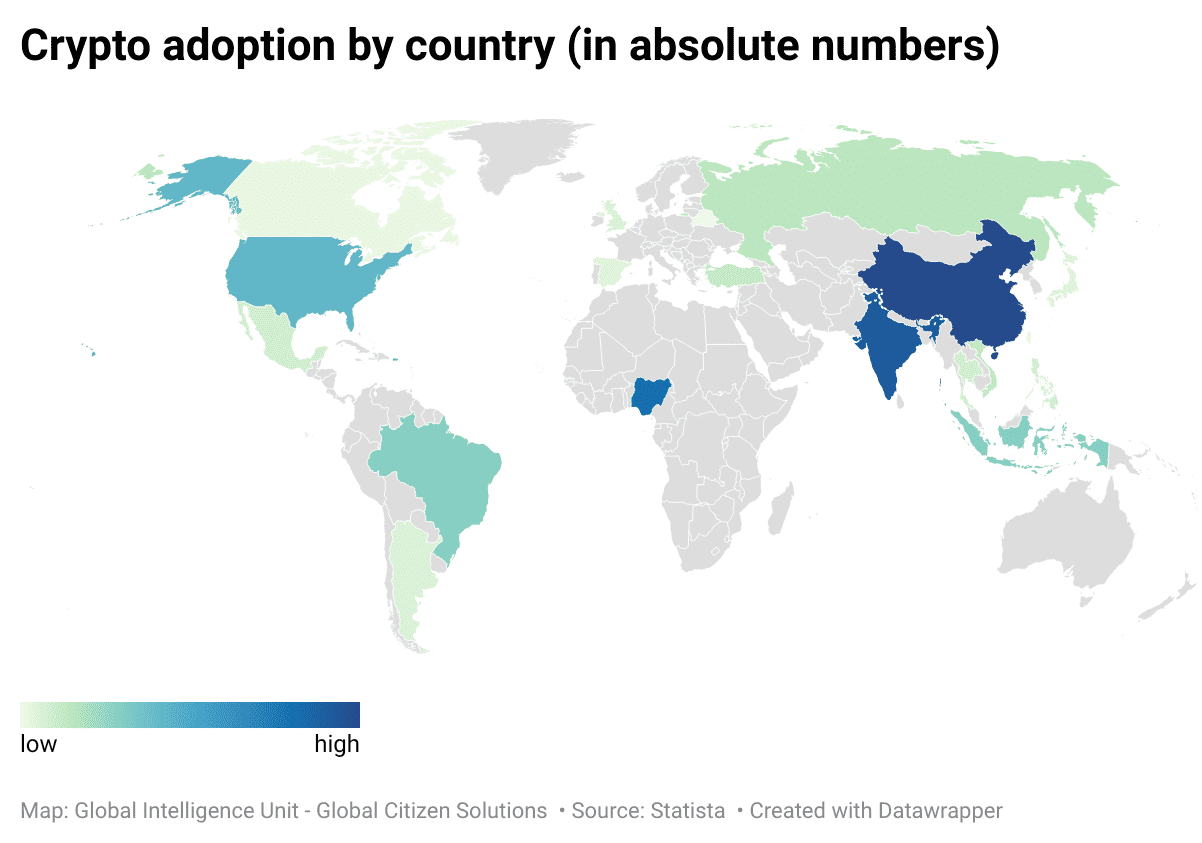
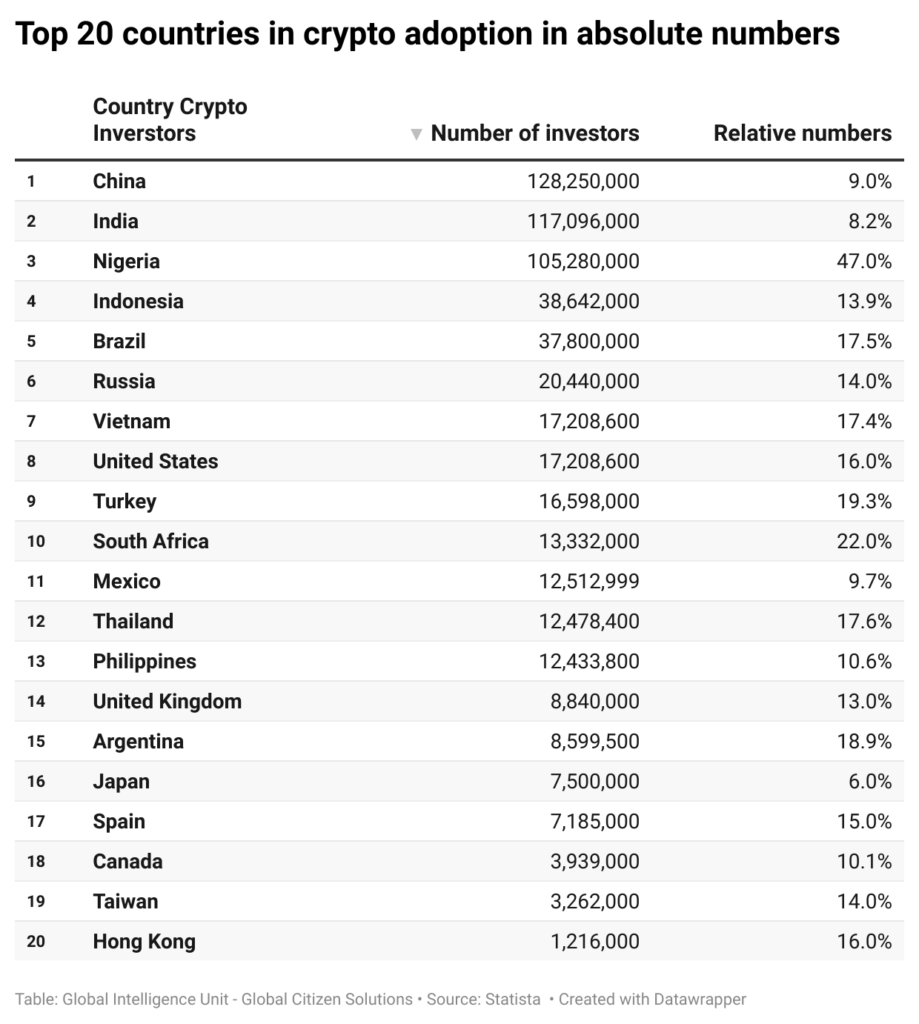
Currently, data on the top countries in crypto adoption reveals that China leads in absolute numbers with approximately 128.25 million crypto investors, representing 9% of its population. India and Nigeria follow closely, with 117.1 million and 105.3 million investors, respectively. While China and India have large populations, which naturally contributes to their high absolute numbers, Nigeria’s position is particularly noteworthy given its smaller population size. This indicates a significant penetration of cryptocurrency in Nigeria, driven by factors such as economic instability and a high level of interest in alternative financial systems.
In terms of relative numbers, Nigeria stands out with 47% of its population investing in cryptocurrencies, the highest among the listed countries. This suggests that nearly half of Nigeria’s population is engaged with digital assets, underscoring the critical role cryptocurrencies play in the country’s financial ecosystem. However, the country still has considerable room for growth, especially as more people seek alternatives to the traditional banking system, which can be unstable or inaccessible in certain regions. With a young, tech-savvy population and growing smartphone penetration, Nigeria is poised to further integrate cryptocurrencies into its financial ecosystem. If economic challenges persist, such as currency devaluation or inflation, the reliance on cryptocurrencies as a store of value and medium of exchange is likely to increase, potentially boosting adoption even further.
In India, where 8.2% of the population currently invests in cryptocurrencies, the potential for growth is immense given the country’s vast population. The government’s evolving stance on crypto regulation could play a pivotal role in shaping future adoption. If regulatory hurdles are clarified or eased, and with the increasing digitalization of the economy, India could see a significant uptick in crypto adoption. Moreover, as more financial services become accessible via mobile platforms, and as awareness about cryptocurrencies spreads, especially in rural areas, India could rapidly become one of the largest markets for crypto in the world.
Other countries with significant relative adoption include Turkey (19.3%), Brazil (17.5%), and Vietnam (17.4%), reflecting similar trends where economic challenges and inflation drive citizens towards cryptocurrencies as a hedge or alternative investment. Interestingly, while countries like the United States and China have massive absolute numbers of investors, their relative adoption rates are more moderate at 16% and 9%, respectively, reflecting their larger, more diversified financial markets where crypto is one of many investment options.
In all these countries, the common thread driving potential growth is the economic environment. Where traditional financial systems are under pressure, and where digital access is expanding, cryptocurrencies are likely to gain further traction. As regulatory frameworks become clearer and more supportive, and as more people become educated about the benefits of digital currencies, the adoption rates in these countries could increase significantly, making them key players in the global crypto market.
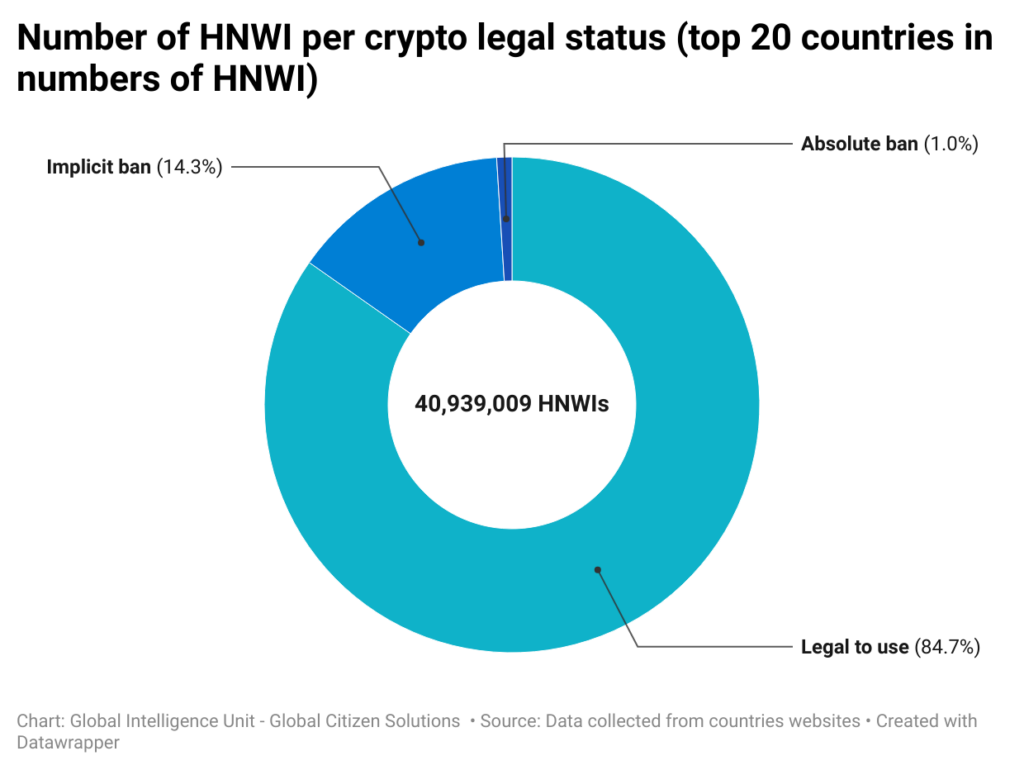
In our analysis of the global landscape of cryptocurrency regulations, we also found that 15 of the 20 countries with the largest numbers of High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) have legalized the use of cryptocurrencies. However, a notable exception exists, 5 of these countries enforce some kind of ban on cryptocurrency usage, mining and exchanging, with China being the most prominent among them imposing a total ban to crypto assets.
China not only leads the world in the number of cryptocurrency investors, but it is also home to the largest population of high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs). However, despite this significant interest and wealth, China is one of the few countries that has imposed a total ban on cryptocurrency activities, including trading and mining. This stringent regulatory stance may push investors to consider relocating to more crypto-friendly jurisdictions such as Hong Kong and Taiwan, where the regulatory environment is more accommodating, allowing for greater freedom in engaging with digital assets.
Born out of the Great Recession, cryptocurrency was initially embraced as a means to decentralize and denationalize money and reduce reliance on central bank powers.6Cointelegraph. (2024, March 21). History of Crypto: Bitcoin — Satoshi Nakamoto’s response to the global financial crisis. Cointelegraph. Retrieved from https://cointelegraph.com/news/satoshi-nakamoto-bitcoin-emergence-financial-crisis Bitcoin aimed to bypass traditional financial controls, oversight, and fees, replacing the legitimacy provided by institutions like banks with cryptographic decentralized networks. Yet, as the market has matured, the call for regulation has grown louder, with both regulators and investors pushing for greater oversight to stabilize this volatile and insecure investment landscape.
The central challenge facing the cryptocurrency market today is finding a balance between the decentralization and freedom that define these digital assets and the safety and guarantees typically provided by centralized systems. Cryptocurrencies were initially celebrated for their ability to operate outside traditional banking systems, offering users anonymity and reduced transaction fees. However, this lack of oversight, while appealing for its freedom and independence, also brings risks, such as increased susceptibility to fraud and criminal activities. Therefore, the task at hand is to synchronize the inherent benefits of decentralized cryptocurrencies with the protective measures and stability of centralized financial systems. This involves developing regulatory frameworks that can accommodate the unique properties of cryptocurrencies while ensuring they are safe, stable, and trustworthy enough to function alongside conventional currencies in the global economy.
Crypto investment: the generational shift
In recent years, a striking trend has emerged in the investment landscape: Millennials and Gen Z are investing in cryptocurrencies at a five times higher rate than their predecessors, concludes a report from Bank of America.7Bank of America Institute. (2022). Study of Wealthy Americans – October 2022. Retrieved from https://institute.bankofamerica.com/content/dam/bank-of-america-institute/economic-insights/study-of-wealthy-americans-october-2022.pdf This generational shift is evident in portfolio allocations, with younger investors (age 21-42) dedicating an average of 15% to cryptocurrencies, compared to a mere 3% by older investors (see chart below). Younger people are 7.5 times more likely to include cryptocurrencies in their investment portfolios and 5 times more likely to feel confident in their understanding of these digital assets. Despite the overall low usage of cryptocurrencies, this significant interest among younger investors suggests a generational shift towards embracing digital and alternative investments. This trend underscores the importance of demographic factors in shaping investment strategies and preferences, highlighting the need for tailored financial advice and products for different age groups.
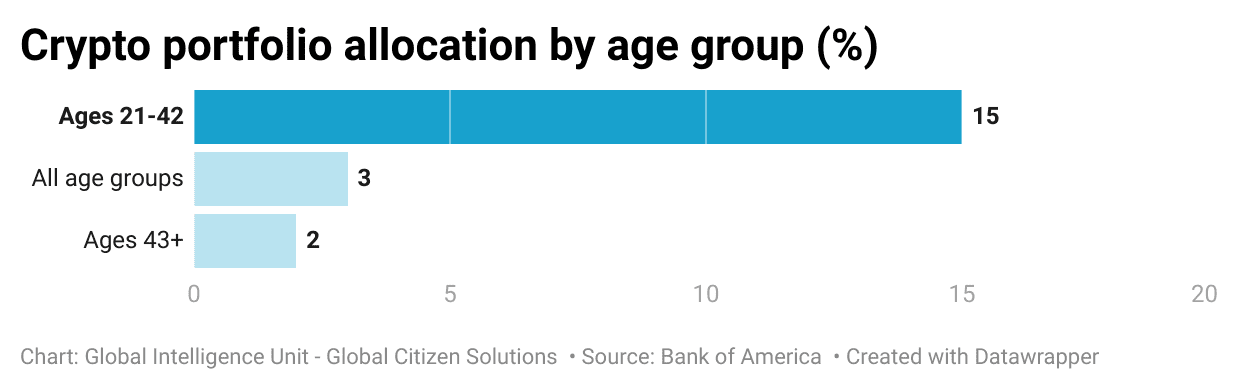
Nearly 29% of younger generations view cryptocurrencies as a significant opportunity for wealth creation, a stark contrast to the 7% of baby boomers who share this sentiment. This growing enthusiasm for digital assets among younger investors signals a broader transformation in investment strategies and priorities.Millennials and Gen Z show a marked preference for entrepreneurial ventures, ESG-focused funds, and direct investments in companies. This trend highlights their inclination towards higher risk but more ethically aligned investments, with the potential for higher rewards.
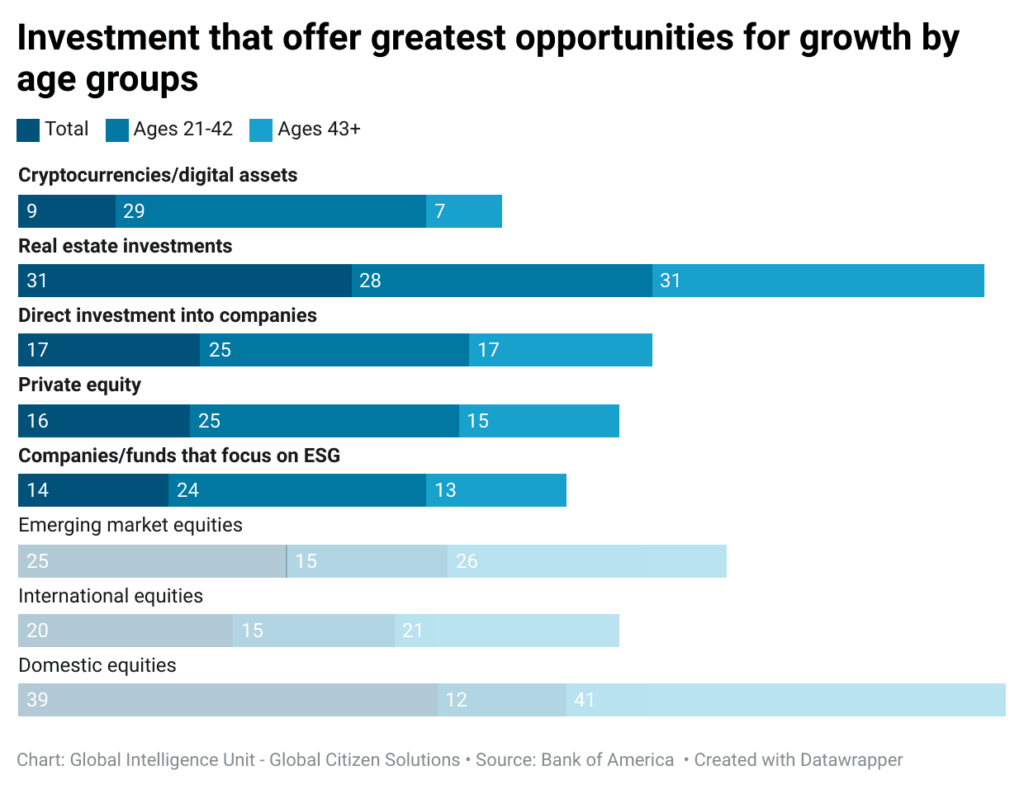
The enthusiasm for cryptocurrencies among younger generations is not just a fleeting trend but part of a larger movement towards digital and alternative investments. This generation’s confidence in traditional asset classes, especially regarding domestic equities, has waned, influenced by economic disruptions and a perception of limited growth potential in conventional stocks and bonds. Cryptocurrencies, with their promise of high returns and revolutionary technology, appeal to Millennials’ and Gen Z’s desire for innovative investment opportunities.
This shift in investment preferences comes at a pivotal time, as the world anticipates the largest wealth transfer in history. By 2045, more than $84 trillion is expected to pass from baby boomers to their descendants (see figure below), marking an unprecedented redistribution of wealth.
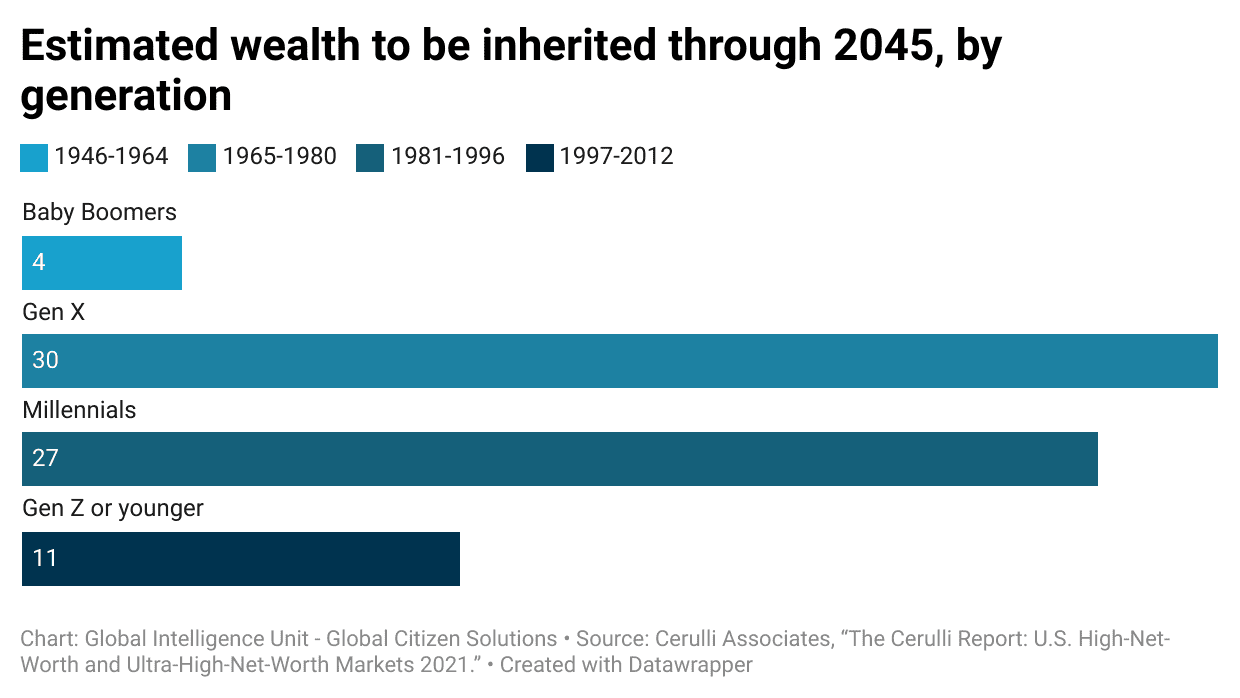
This massive transfer underscores the growing influence of younger generations (Millennials and Gen X and Z) in the financial markets. Their preference for cryptocurrencies and other digital assets suggests that the future of investment will be increasingly digital and decentralized.
Based on current trends and generational wealth data, we can anticipate a significant increase in cryptocurrency investments over the next decade. Millennials and Gen Zs, who are poised to inherit a combined total of $38 trillion through 2045, are particularly inclined towards digital assets. With an estimated 15% of their wealth expected to be directed towards cryptocurrencies, this translates to an investment of approximately $5.7 trillion. This figure alone suggests that the crypto market could see at least double the current investment levels. Furthermore, as awareness of the market grows and regulatory frameworks evolve to provide greater accountability and security, we can expect an even greater influx of investments.
The trend towards digital asset investment among Millennials and Gen Zs is also closely linked to the rise of global mobility and the digital nomad lifestyle. Younger generations are increasingly living as digital nomads8Malik, Z. (2022, April 26). Over 1 billion digital nomads by 2035. International Accounting Bulletin. Retrieved from https://www.internationalaccountingbulletin.com/features/over-1-billion-digital-nomads-by-2035/. See also Global Digital Nomad Report at: https://www.globalcitizensolutions.com/intelligence-unit/reports/global-digital-nomad-report/#methodology, seeking to relocate for better quality of life and more lucrative investment opportunities. Investment migration has become a viable option, particularly in countries with growing wealth but less powerful passports, such as Iran, India and Vietnam and some countries in Africa and Latin America.9Global Citizen Solutions. (2023). Global Passport Index 2023. Retrieved from https://www.globalcitizensolutions.com/passport-index/
Another interesting case that links investment in crypto and relocation is China. Despite recent advancements in the Chinese crypto landscape, such as the development of innovative blockchain projects10Shin, E. (2024, May 26). Best Chinese crypto projects. Datawallet. Retrieved from https://www.datawallet.com/crypto/best-chinese-crypto-projects, digital assets remain prohibited in mainland China. This regulatory environment has compelled many Chinese investors seeking to engage in digital asset trading to invest primarily in Hong Kong.11Bloomberg, (2024, April 30). ChinaAMC sees Hong Kong crypto ETFs opening door for Chinese investors. Bloomberg. Retrieved from https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-04-30/chinaamc-sees-hong-kong-crypto-etfs-opening-door-for-chinese-investors Hong Kong’s regulatory framework is more accommodating to cryptocurrency activities, offering Chinese investors the opportunity to participate in the crypto market without the stringent restrictions and potential legal repercussions present in mainland China. This migration allows investors to leverage Hong Kong’s more progressive stance on digital assets, thereby accessing a broader array of investment opportunities and capitalizing on the region’s supportive infrastructure for cryptocurrency trading.
However, the younger generations’ investment strategies are not solely driven by the pursuit of high returns. Millennials and Generation Z are also championing principles of accountability, due diligence, and responsible investing. They are not only seeking financial gains but also demanding greater transparency and ethical standards in their investments. This dual focus on profitability and principled investing is reshaping the financial landscape, pushing for more sustainable and socially responsible investment practices.
The trend towards digital asset investment among younger generations is a clear indication of their evolving priorities and values. As they prepare to inherit significant wealth, their investment choices will play a crucial role in shaping the future of finance. With nearly a third of younger investors viewing cryptocurrencies as a prime opportunity for wealth creation and maintenance and dedicating a substantial portion of their portfolios to these digital assets, the financial industry must adapt to meet the demands of this new generation. The rise of cryptocurrencies, coupled with a more mobile lifestyle highlights a profound shift towards a more innovative, accountable, and inclusive financial future.
Overall Crypto Regulations
As the cryptocurrency market continues to grow and evolve, the need for comprehensive regulation becomes increasingly apparent. Calls for the adoption of regulations governing the issuance, provision, and exchange of crypto assets are being voiced by various sectors. According to Andrea Enria, the Chair of the Supervisory Board of the European Central Bank (EBC), “the turbulence experienced in crypto markets since its inception (…) makes a strong case for a tougher regulatory approach”12Enria, A. (2023, November 14). Regulating crypto finance: Taking stock and looking ahead. European Central Bank. Retrieved from https://www.bankingsupervision.europa.eu/press/speeches/date/2023/html/ssm.sp231114~fd1b2cc234.en.html. In the same vein, investors and wealth managers are calling for more transparent regulations in the cryptocurrency market to offer a broader range of products to their clients.13Oliver, J. (2024, April 30). Crypto demand from wealthy clients puts pressure on managers. Financial Times. Retrieved from https://channels.ft.com/en/ft-wealth/crypto-demand-from-wealthy-clients/ This demand is driven by the increasing pressure from younger generations of wealthy clients who are eager to invest in digital assets.
Key areas that demand regulatory attention include Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF), consumer protection, and market integrity. Implementing robust AML and CTF measures is crucial to prevent cryptocurrencies from being used for illicit activities. By requiring exchanges and service providers to verify customer identities and report suspicious activities, regulators can help maintain the integrity of the financial system. Additionally, Know Your Customer (KYC) processes play a vital role in crypto compliance measures, ensuring that entities can verify the identity of their users and prevent fraudulent activities.
Consumer protection is another critical area where regulation is essential. The cryptocurrency market has seen its share of fraud, scams, Ponzi schemes and other malicious activities that can harm investors and users.14Rathnam, L. (2024, April 2). The 10 biggest scandals that rocked the blockchain world. Planet Compliance. Retrieved from https://www.planetcompliance.com/top-10-scandals-rocked-blockchain-world/ Transparent and fair practices by exchanges, wallet providers, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are necessary to build trust and protect consumers. Regulatory oversight can ensure that these entities operate with integrity and that users are safeguarded against potential losses.
Market integrity and fraud prevention are paramount to ensuring a fair and transparent cryptocurrency market. Monitoring trading practices and enforcing rules helps maintain a level playing field, fostering a healthy market environment. In this regard, lately we have seen many regions around the world increasingly focusing on implementing regulation for crypto assets to bring more stability and security to the sector.
North America, particularly the United States and Canada, leads in the legal acceptance of cryptocurrencies, with established regulatory frameworks that support the use and trading of digital assets, fostering their integration into financial systems. Europe follows closely, as member states work towards a unified regulatory framework, such as the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCAR) regulation, which aims to provide legal clarity and protect investors while encouraging innovation. In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea stand out for their proactive approach to cryptocurrency regulation and integration, contrasting with China that has deemed crypto-assets illegal in 2021. Latin America has a mixed regulatory stance, but countries like El Salvador have made significant strides by adopting Bitcoin as official legal tender. Australia, in the Oceania region, also exemplifies a supportive legal environment for cryptocurrencies, balancing innovation with consumer protection through clear regulations.
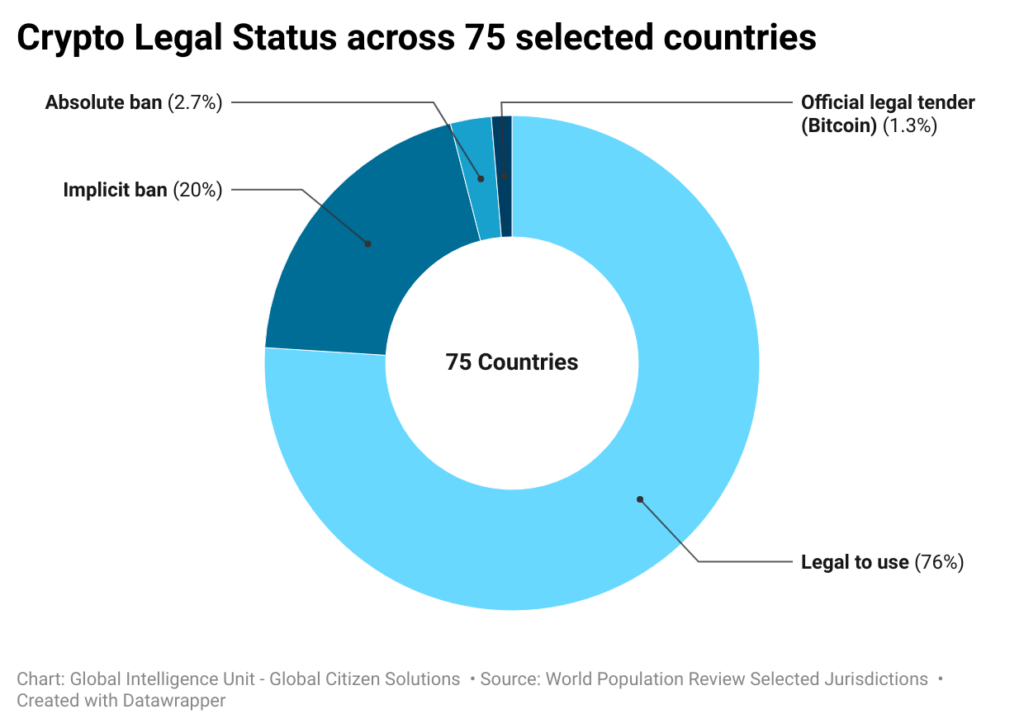
A significant majority of countries 76% (57 selected jurisdictions) have deemed cryptocurrencies legal to use (chart below), indicating a global trend towards acceptance and integration of digital assets into financial systems. However, 20% of countries (15 countries) have implemented implicit bans, meaning that while cryptocurrencies are not outright illegal, there are significant restrictions that limit their use. These restrictions may include prohibiting financial institutions from offering crypto-related services, banning or imposing strict licensing on exchanges, restricting advertising and promotion, imposing hefty taxes and complex reporting requirements, creating legal uncertainty. These measures create a hostile environment that discourages investment and use of cryptocurrencies without formally declaring them illegal.
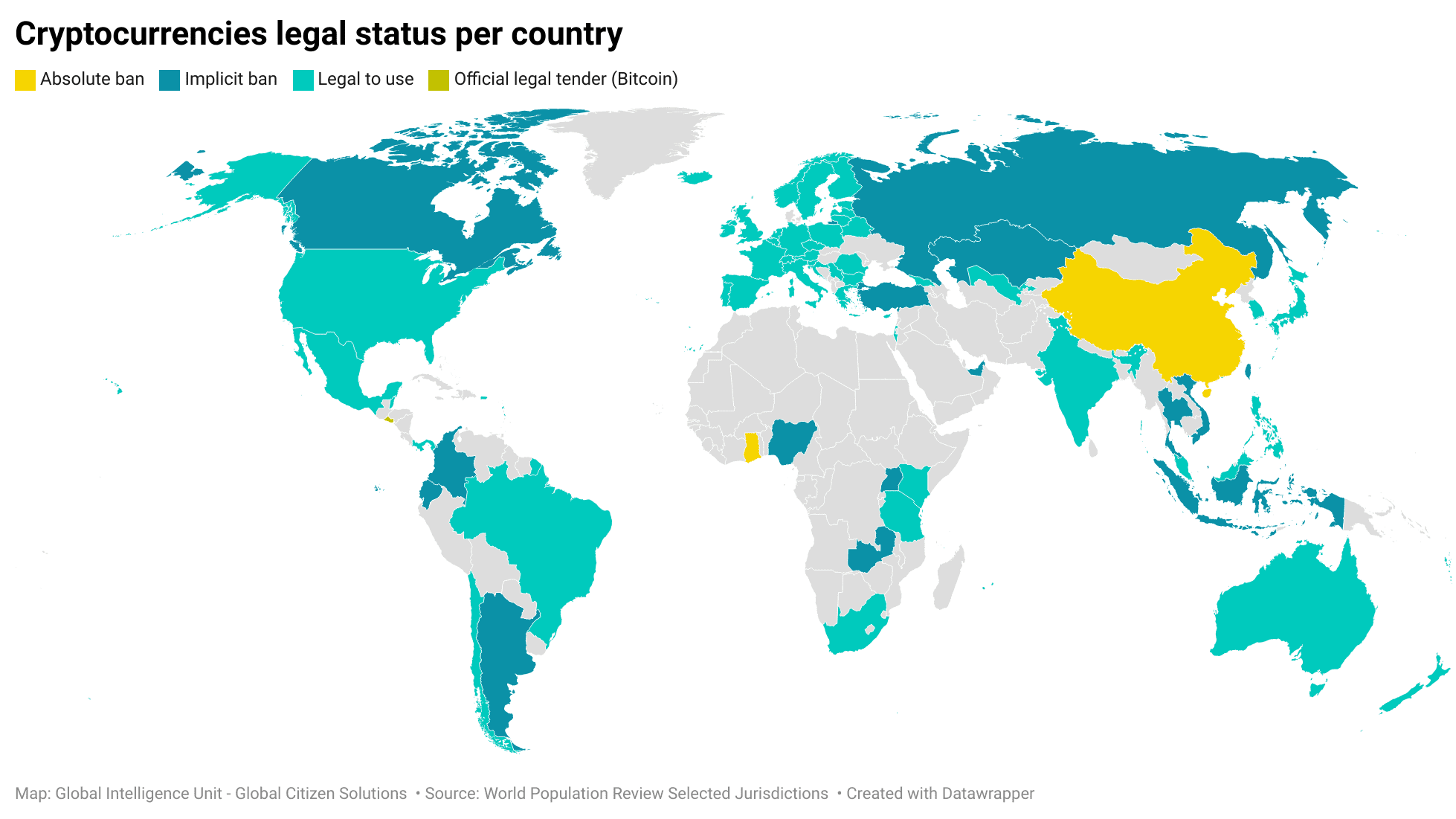
Russia, for instance, has not outright banned cryptocurrencies, but it has imposed significant restrictions that create a challenging environment for their use. In the past, the Russian government has introduced laws that prohibit the use of cryptocurrencies as a means of payment.15Cryptocurrency.law. (2023, December 9). Cryptocurrency regulation in Russia: The 2024 outlook. Retrieved from https://cryptocurrency.law/cryptocurrency-regulation-in-russia-the-2024-outlook/ Additionally, stringent regulations have been imposed on cryptocurrency exchanges and ICOs, requiring them to register and comply with various legal and financial standards. In a recent development, the Duma is reportedly set to ban the circulation of cryptocurrencies starting September 1, 2024, allowing only domestic digital assets.16CryptoGlobe. (2024, April 29). Russia reportedly set to ban cryptocurrency circulation from September 1, allowing only domestic digital assets. Retrieved from https://www.cryptoglobe.com/latest/2024/04/russia-reportedly-set-to-ban-cryptocurrency-circulation-from-september-1-allowing-only-domestic-digital-assets/ This legislation, spearheaded by Anatoly Aksakov, Chairman of the State Duma Committee on the Financial Market, aims to prohibit the organization and circulation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin within Russia. The decision is driven by concerns over cryptocurrencies acting as quasi-currencies that could undermine the ruble’s role as the national monetary unit.
Additionally, 2.7% of countries have absolute bans, completely prohibiting the use of cryptocurrencies. China, for instance, imposed a comprehensive ban on crypto transactions and mining in September 2021, aiming to curb illicit financial activities. A small fraction (1.3%) has adopted Bitcoin as an official legal tender.
It becomes evident that while there is a growing acceptance of cryptocurrencies globally, there remains considerable divergence in regulatory approaches. Regions with established financial markets, like North America and Europe, are more inclined towards regulation and integration rather than outright prohibition.
Regional Regulations
Europe
In Europe, the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCAR)17European Parliament and Council of the European Union. (2023, June 9). Regulation (EU) 2023/1114 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31 May 2023 on markets in crypto-assets, and amending Regulations (EU) No 1093/2010 and (EU) No 1095/2010 and Directives 2013/36/EU and (EU) 2019/1937. Official Journal of the European Union, L 150, 40-205. Retrieved from https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/1114/oj came into force in July 2023 as the first comprehensive cross-jurisdictional framework aimed at regulating crypto-assets. It will be applicable in full by the end of 2024. MiCAR is designed to harmonize the regulatory approach across EU member states, replacing disparate national frameworks with a unified system that includes strict rules for crypto-asset service providers (CASPs) and issuers (CAIs).
The EU’s approach to cryptocurrency regulation is guided by principles that ensure financial and market integrity, consumer protection, and overall financial stability.18European Parliament and Council of the European Union. (2023, June 9). Regulation (EU) 2023/1114 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31 May 2023 on markets in crypto-assets, and amending Regulations (EU) No 1093/2010 and (EU) No 1095/2010 and Directives 2013/36/EU and (EU) 2019/1937. Official Journal of the European Union. Retrieved from https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX%3A32023R1114 The implementation of the Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (5AMLD) in January 202019European Parliament and Council of the European Union. (2018, May 30). Directive (EU) 2018/843 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 amending Directive (EU) 2015/849 on the prevention of the use of the financial system for the purposes of money laundering or terrorist financing, and amending Directives 2009/138/EC and 2013/36/EU. Official Journal of the European Union. Retrieved from https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2018/843/oj marked a significant step, bringing cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers under stringent AML/CTF requirements. These measures are designed to mitigate the risks associated with the pseudonymous nature of digital assets.
According to the European Securities and markets Authority (ESMA), MiCAR sets out to achieve several key objectives. First, it aims to enhance consumer and investor protection by enforcing transparency requirements and mandating detailed disclosures for crypto-asset issuers. Second, MiCAR seeks to prevent market abuse and ensure the orderly functioning of crypto-asset markets by implementing measures to combat insider trading and market manipulation. Third, the regulation aims to address the systemic risks posed by certain digital assets to financial stability, particularly stablecoins, by setting prudential requirements for issuers and significant market participants.20European Securities and Markets Authority. (2023, October). Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) Consultation Paper – 2nd package (ESMA75-453128700-438). Retrieved from https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2023-10/ESMA75-453128700-438_MiCA_Consultation_Paper_2nd_package.pdf
Additionally, the ECB officials have expressed support for MiCAR. The banks’ President Christine Lagarde emphasized the importance of regulatory frameworks like MiCAR in ensuring that cryptocurrencies do not undermine financial stability. She noted, “Crypto assets are bringing about new challenges in terms of investor protection, market integrity, and financial stability. MiCAR will provide the necessary safeguards and clear rules for the industry to develop responsibly”.21Lagarde, C. (2024, April 22). Unlocking the power of ideas. European Central Bank. Retrieved from https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/key/date/2024/html/ecb.sp240422~0f3299e7bb.en.html
By providing a clear and predictable regulatory environment, MiCAR aims to attract investment and innovation in the digital asset space. This regulation sets a benchmark for other jurisdictions seeking to regulate cryptocurrencies effectively, promoting a more stable and transparent global crypto market.22Enria, A. (2023, November 14). Regulating crypto finance: Taking stock and looking ahead. European Central Bank. Retrieved from https://www.bankingsupervision.europa.eu/press/speeches/date/2023/html/ssm.sp231114~fd1b2cc234.en.html[6] However, the increased regulatory burden may pose challenges for smaller players, potentially leading to industry consolidation as businesses strive to meet the new compliance requirements.
The United Kingdom, despite not under MiCAR framework, is also taking significant steps to regulate the cryptocurrency sector. Recognizing the need for a robust framework to ensure financial stability and consumer protection, the UK government has mandated that any company offering digital currency services must be authorized by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).23Pritchard, S. (2023, April 25). Regulation of digital assets in the UK. Financial Conduct Authority. Retrieved from https://www.fca.org.uk/news/speeches/regulation-digital-assets-uk “The government’s position is that firms dealing directly with UK retail consumers should be required to be authorized irrespective of where they are located,” stated the UK finance ministry.24Shine, I. (2024, May 2). How are crypto regulations changing around the world? World Economic Forum. Retrieved from https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/05/global-cryptocurrency-regulations-changing/[8] This approach aims to prevent regulatory arbitrage, ensuring that all companies, whether domestic or international, adhere to the same standards when operating within the UK market.
In addition to general cryptocurrency regulations, the FCA and the Bank of England have proposed specific regulations for stablecoins.25Bank of England. (2023, November 6). Regulatory regime for systemic payment systems using stablecoins and related service providers: Discussion paper. Retrieved from https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/paper/2023/dp/regulatory-regime-for-systemic-payment-systems-using-stablecoins-and-related-service-providers This proposal aims to ensure that stablecoins can operate within a secure and regulated environment, addressing issues related to financial stability and consumer protection.
The steady rise in adoption can be attributed to several factors, including greater awareness of the potential of blockchain technology, the proliferation of user-friendly investment platforms, and a growing desire among younger generations to diversify their financial portfolios. Despite the UK’s stringent regulatory environment, which emphasizes transparency and compliance, investors have shown resilience and adaptability, driving the market forward.
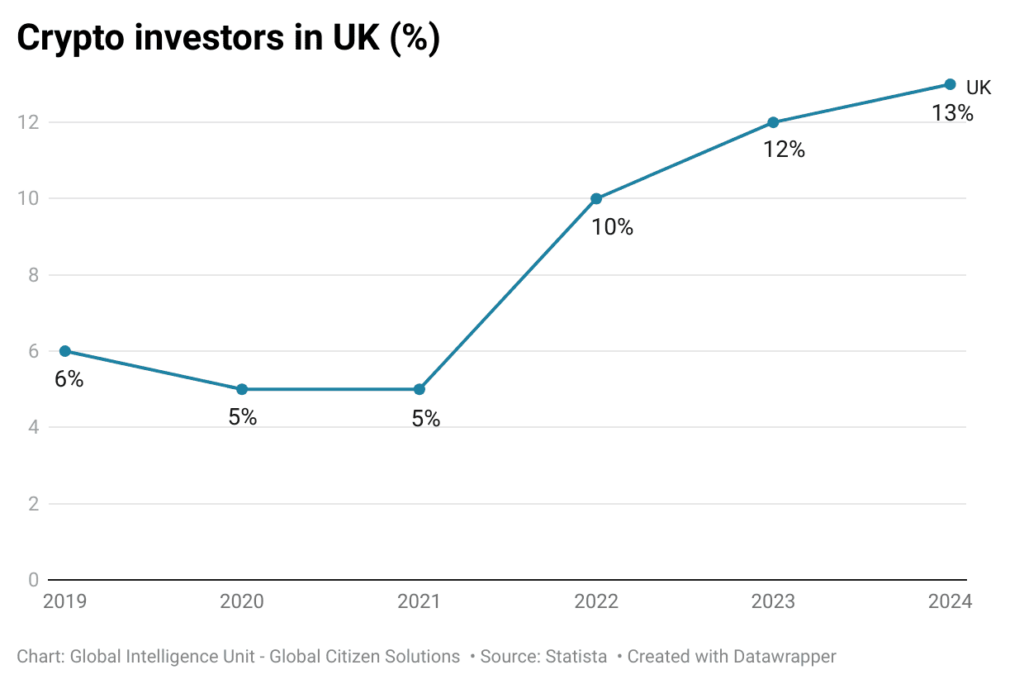
Over the past five years, the United Kingdom has witnessed a notable surge in cryptocurrency adoption, marking a significant shift in how digital currencies are perceived and used across the country. Starting at just 6%, the percentage of UK nationals involved in crypto investments has more than doubled, reaching 13% (see chart below). This growth reflects not only an increasing public interest in digital assets but also a broader acceptance of cryptocurrencies as viable investment options.
Tax-wise, the UK has a clear framework for how cryptocurrency transactions are taxed. The country imposes capital gains tax on profits made from selling crypto assets, with the tax rate depending on your overall income. For the tax year 2023/24, the capital gains tax allowance is £6,000, which will be reduced to £3,000 in 2024/25. This allowance applies to all capital gains, not just those from cryptocurrency.
Income from crypto activities such as staking, mining, or airdrops is also taxable and is added to your regular income for the year. The UK does provide some tax relief, such as tax-free gifts of crypto between spouses and the ability to offset losses against gains. However, the country’s approach to taxing crypto can be seen as less favorable compared to some jurisdictions with more lenient tax regimes.
While the UK is becoming increasingly crypto-friendly in terms of adoption and regulation, it also enforces strict tax and compliance rules. Recent changes to the UK’s non-dom legislation have tightened residency rules, making it more challenging for long-term residents to maintain non-dom status. Specifically, individuals who have lived in the UK for 15 out of 20 years are now deemed domiciled, making them liable for UK taxes on their worldwide income and gains. This significantly impacts crypto investors who can no longer shelter offshore crypto gains from UK taxation under the remittance basis, resulting in tax liabilities on all crypto holdings, including those held offshore.
The remittance basis previously allowed non-doms to avoid UK taxes on income kept offshore, but now, stricter scrutiny and reporting requirements mean that any crypto-derived income brought into the UK will be taxed. This has made it crucial for non-dom crypto investors to be strategic about when and how they remit their crypto gains, as these remittances are now subject to closer examination by UK tax authorities. These changes may prompt some investors to consider offshore structuring or reevaluate their residency status to maintain a favorable tax position, though these options come with complexities and risks.
Regional Considerations
- Switzerland remains one of the most attractive destinations for crypto investors due to its favorable tax treatment of cryptocurrency gains. The country offers exemptions on crypto profits under certain conditions, making it a highly tax-efficient jurisdiction for long-term investors.
- Liechtenstein offers a crypto-friendly regulatory environment coupled with favorable tax policies, including the exemption of cryptocurrency gains from taxation. This makes it an appealing option for investors seeking both regulatory stability and tax efficiency.
- Portugal has historically been one of the most tax-friendly countries in Europe for crypto investors, with exemptions on personal cryptocurrency gains. Although recent discussions suggest potential changes, Portugal still remains an attractive destination for those looking to minimize tax liabilities on crypto investments.
- Malta is known for its robust regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies, which includes clear guidelines and favorable tax treatments for digital assets. Investors can benefit from Malta’s comprehensive approach to regulation while enjoying a competitive tax regime.
- Estonia offers a favorable tax environment where crypto transactions are generally not subject to capital gains tax for individuals. Coupled with a progressive regulatory framework, Estonia provides a balanced environment for crypto investors looking for both tax efficiency and regulatory clarity.
- With the introduction of MiCAR, investors should consider how this regulation will harmonize the crypto landscape across EU member states. While MiCAR aims to provide regulatory certainty, its implementation might introduce additional compliance costs. Investors should evaluate how MiCAR will impact their investments and consider jurisdictions within the EU that offer the most favorable conditions under the new framework.
Recommendations
- While MiCAR aims to create a unified regulatory framework, the tax treatment of cryptocurrencies still varies significantly across EU member states. The EU could work towards harmonizing crypto tax policies, providing clear, consistent, and investor-friendly tax guidelines that apply uniformly across the region.
- To attract and retain crypto investors, European countries could introduce tax incentives for long-term cryptocurrency holdings. This could include lower capital gains tax rates for assets held over a certain period or exemptions for specific types of crypto activities, such as staking or earning interest on crypto assets.
- The current reporting requirements for cryptocurrency transactions can be cumbersome and complex. Simplifying these requirements, possibly through standardized digital reporting systems across the EU, would make it easier for investors to comply with tax regulations, reducing the administrative burden and encouraging more individuals and businesses to invest in cryptocurrencies.
- As the crypto space evolves, new forms of activities like DeFi, NFTs, and crypto lending are gaining popularity. The EU could improve its legislative environment by developing clear, forward-looking guidelines for these emerging areas, ensuring that they are regulated in a way that fosters innovation while protecting investors.
- Encouraging collaboration between governments, regulatory bodies, and the crypto industry could lead to more informed and effective regulation.
- Regular consultations with industry experts and stakeholders would ensure that the regulatory framework evolves in line with the market’s needs, making Europe more attractive to crypto investors.
Americas
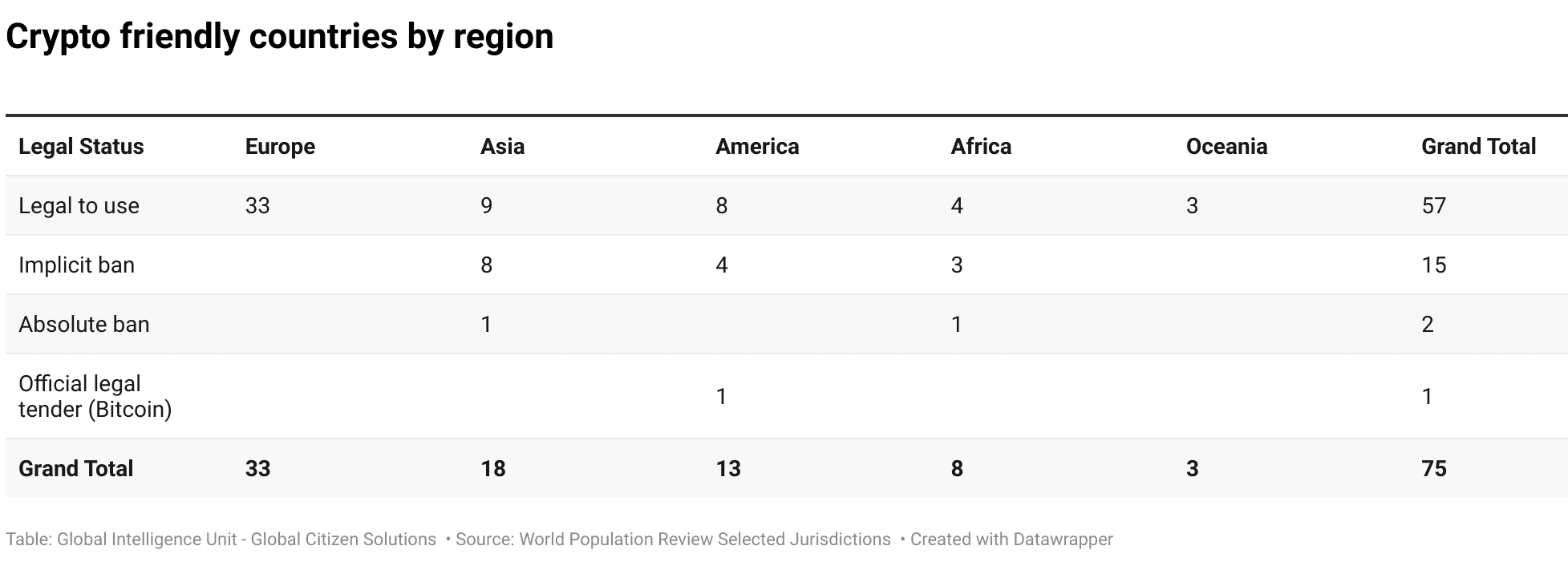
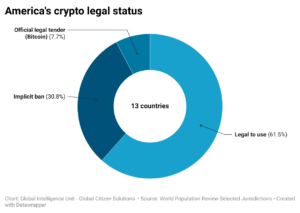
The continent’s approach to digital assets ranges from full legalization and integration into the financial system to outright bans, with a significant number of nations adopting a cautious middle ground through implicit bans (see chart below). We analyzed the legal status of cryptocurrencies across 13 countries in the Americas, from which a substantial majority, 61,5% (8 countries), have adopted legal frameworks that permit the use of cryptocurrencies. This group includes significant economies like Canada, Brazil, and Argentina, as well as numerous Caribbean nations such as Bermuda and the Cayman Islands.
Brazil, for instance, has become one of the leading countries in cryptocurrency adoption, consistently ranking high globally. The country’s vibrant crypto market is driven by a combination of factors, including a large population with increasing access to digital technologies, economic instability that prompts the search for alternative assets, and a strong interest in innovative financial solutions. As of 2024, Brazil remains the largest crypto market in Latin America and second in public adoption of cryptocurrencies in the Americas, surpassed only by the US, with substantial growth in trading volumes and a growing number of crypto users across various demographics.
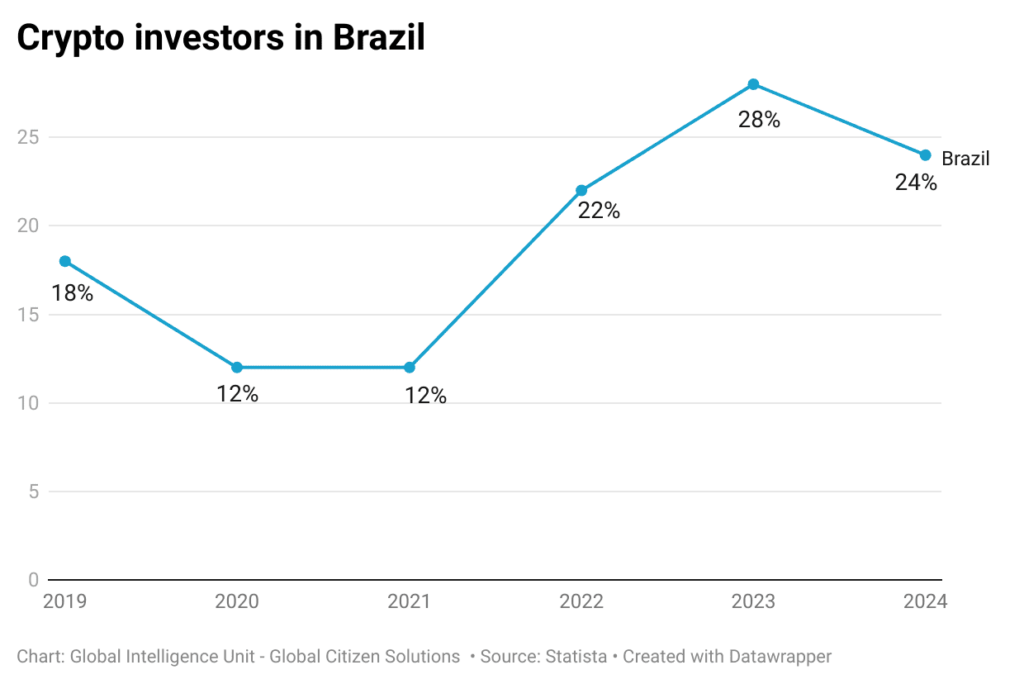
Nevertheless, Brazil’s tax regime for cryptocurrencies is notably stringent, imposing capital gains taxes that range from 15% to 22.5%, which can be a considerable burden for investors, especially those with large portfolios or who engage in frequent transactions. The comprehensive tax obligations extend to all cryptocurrency activities, including capital gains, income from mining or staking, and even transfers between wallets and exchanges. Investors are required to meticulously report these activities, adding complexity to their tax management. The introduction of a 15% tax on earnings from cryptocurrencies held on foreign exchanges further complicates the landscape. Unlike some countries that offer tax incentives to attract crypto investment, Brazil provides no such incentives, focusing instead on stringent regulation and thorough taxation of the market.
For investors, Brazil offers a well-regulated environment with clear guidelines under the Virtual Assets Act, which came into effect in 2023. This legislation outlines the requirements for virtual asset service providers (VASPs), including obtaining licenses from the Central Bank of Brazil and complying with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. While this regulatory framework provides a secure environment for crypto transactions, it also imposes significant compliance obligations on investors and service providers, making it essential for crypto investors to stay informed and compliant with the latest regulations.
Implicit ban is imposed in 4 jurisdictions (30.77%) in the selected nations in Americas. Countries like Colombia and Ecuador fall into this category. While they do not outright prohibit the use of digital assets, they impose stringent regulations that effectively limit their use.
In Colombia, the regulatory framework requires financial institutions to refrain from engaging in or facilitating transactions involving cryptocurrencies.26Freeman Law. (2024). Colombia and cryptocurrency. Retrieved from https://freemanlaw.com/cryptocurrency/colombia/ Ecuador, on the other hand, has imposed restrictions on the use of cryptocurrencies within its banking system, reflecting similar concerns about financial integrity and consumer protection.
Bolivia and the Dominican Republic have chosen to completely prohibit any activities involving digital currencies, citing significant apprehensions about the volatility and potential misuse of cryptocurrencies. Bolivia’s absolute ban, enacted in 2014, was driven by concerns over the potential for cryptocurrencies to facilitate illegal activities and undermine financial stability.27Willing, N. (2024, March 4). Cryptocurrency bans explained: Which countries have restricted crypto and why?Techopedia. Retrieved from https://www.techopedia.com/cryptocurrency-bans-explained-which-countries-have-restricted-crypto The Dominican Republic has similarly banned the use of cryptocurrencies28Freeman Law. (2024). The Dominican Republic and cryptocurrency. Retrieved from https://freemanlaw.com/cryptocurrency/dominican-republic-and-cryptocurrency/, reflecting a conservative stance towards the integration of digital assets into the national financial system. These absolute bans highlight the challenges and risks perceived by regulators in adopting cryptocurrencies.
The United States operates a ‘dual banking system,’ where digital asset services can be regulated at both the state and federal levels. This system allows for a nuanced approach to overseeing digital asset activities, addressing the complexities inherent in the rapidly evolving crypto market. Both state and federal regulatory and enforcement agencies have proactively moved to regulate digital asset activities, often outpacing legislative actions from Congress and the White House.29Herzog, P. (2024, February 2). Navigating US state crypto policy developments in 2024. Crypto for Innovation. Retrieved from https://cryptoforinnovation.org/navigating-us-state-crypto-policy-developments-in-2024/ This proactive stance involves using existing legal frameworks and authorities to bring digital assets under regulatory scrutiny.
At the state level, various states have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for digital assets. For example, New York’s BitLicense requires digital currency businesses to obtain a specific license from the New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS).30Oxford Business Group. (2023, December 4). Emerging markets lead uptake of cryptocurrency despite bear market. Retrieved from https://oxfordbusinessgroup.com/articles-interviews/emerging-markets-lead-uptake-of-cryptocurrency-despite-bear-market This regulation covers activities such as receiving or transmitting virtual currency, performing exchange services, and securing custody of digital assets. This stringent regulatory framework is designed to ensure consumer protection and maintain market integrity within the state.
Similarly, California has implemented legislation that requires crypto service providers to obtain licenses from the state’s Department of Financial Protection and Innovation (DPFI).31Department of Financial Protection and Innovation. (2024). Digital Financial Assets Law. Retrieved from https://dfpi.ca.gov/dfal/#:~=Beginning%20July%201%2C%202025%2C%20companies,a%20license%20from%20the%20DFPI This move signifies a step towards more rigorous regulatory oversight amid concerns about ‘crypto contagion,’ which has been cited as a factor in several bank failures and operational wind-downs throughout 2023. By enforcing these regulations, California aims to mitigate risks and enhance the stability of its financial markets.
Federally, agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) play crucial roles in regulating different aspects of digital assets. The SEC oversees digital assets that are deemed securities, ensuring that they comply with securities laws to protect investors and maintain fair markets. The CFTC regulates digital assets considered commodities, focusing on market integrity and preventing fraudulent practices. FinCEN enforces AML/CFT measures under the Bank Secrecy Act, requiring crypto exchanges to enforce KYC and CTR (Currency Transaction Reporting) compliance.
Recent legislative initiatives have sought to provide clarity and enhance oversight of the digital asset space. The Clarity for Payment Stablecoins Act32Library of Congress. (n.d.). H.R.4766 – 118th Congress (2023-2024): A bill to amend the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 to require certain disclosures relating to short sales, and for other purposes. Congress.gov. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/4766 of 2023 proposes specific regulatory conditions for stablecoin issuers, reflecting an increased acceptance of these digital assets in the financial system. Additionally, the Market Structure Act33Library of Congress. (2023). H.R.4741 – To amend the Consumer Financial Protection Act of 2010 to provide for whistleblower incentives and protection. Library of Congress. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/house-bill/4741 and the Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act34Library of Congress. (2023). Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act, H.R.4763, 118th Congress. Retrieved from https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/4763[9] seek to delineate the regulatory responsibilities of the CFTC and the SEC over digital assets. These efforts are crucial for eliminating regulatory ambiguities and fostering a clear and predictable regulatory environment. Complementing these legislative efforts, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has issued new tax reporting guidelines, and the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) has introduced new accounting standards35Financial Accounting Standards Board. (2023). Accounting for and disclosure of crypto assets. Retrieved from https://www.fasb.org/page/PageContent?pageId=/projects/recentlycompleted/accounting-for-and-disclosure-of-crypto-assets.html aimed at improving transparency and simplifying compliance in the digital asset space.
Notably, 1 country in the Americas has taken the unprecedented step of recognizing cryptocurrency as official legal tender. El Salvador stands out globally for its decision to adopt Bitcoin as an official currency.36Beyer, R. (2024, January 29). El Salvador adopted Bitcoin as an official currency; Salvadorans mostly shrugged. Yale Insights. Retrieved from https://insights.som.yale.edu/insights/el-salvador-adopted-bitcoin-as-an-official-currency-salvadorans-mostly-shrugged This bold move, initiated in 2021, aimed at boosting financial inclusion, attract foreign investment, and leverage the benefits of blockchain technology. El Salvador’s adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender has been met with both enthusiasm and skepticism (see also pages 22 to 26). Proponents argue that it will enhance financial accessibility for the unbanked population and stimulate economic growth.37Patel, R. (2024). Economic freedom or crypto-colonialism? Materialities of Bitcoin adoption in El Salvador. Geoforum, 151, 103980. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0016718524000411 Critics, however, raise concerns about the volatility of Bitcoin and its potential impact on the country’s financial stability.38UNU-MERIT. (2023). El Salvador’s Bitcoin policy: Regret or reward? Retrieved from https://www.merit.unu.edu/el-salvador-bitcoin-policy/ Despite these challenges, El Salvador’s experiment with Bitcoin continues to be closely watched by the global community as a potential model for cryptocurrency integration.
Regional Considerations
- While Brazil imposes significant taxes on cryptocurrency activities, the country’s clear regulatory framework under the Virtual Assets Act provides a secure environment for investments. Investors should carefully manage their tax obligations by keeping meticulous records and considering the potential benefits of Brazil’s large and growing crypto market, which may outweigh the tax costs.
- Investors seeking favorable tax environments should consider jurisdictions like Bermuda and the Cayman Islands, which have established legal frameworks permitting the use of cryptocurrencies with relatively lenient tax regimes. These countries offer attractive conditions for both individual and institutional investors looking to minimize tax liabilities.
- The U.S. offers a complex but robust regulatory environment for digital assets, with both state and federal frameworks providing investor protection and market integrity. Investors should explore states like New York and California, which have specific licenses and regulations that ensure a high level of consumer protection, although this comes with compliance costs.
- El Salvador’s recognition of Bitcoin as legal tender presents unique opportunities for crypto investors, particularly those interested in leveraging blockchain technology for financial inclusion. However, investors should remain cautious about the risks associated with Bitcoin’s volatility and the experimental nature of this initiative.
- Argentina’s economic challenges have driven a high rate of cryptocurrency adoption, making it an attractive market for crypto investments. Investors should consider the potential for growth in Argentina’s crypto market but remain aware of the risks posed by the country’s economic volatility and the regulatory landscape.
- Investors should steer clear of countries like Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, and the Dominican Republic, where stringent regulations or outright bans significantly limit or prohibit cryptocurrency activities. The regulatory risks in these countries outweigh the potential benefits, making them less attractive for crypto investments.
Recommendations
- A significant challenge for crypto investors in the Americas is the patchwork of regulations that vary widely from country to country. Regional collaboration to create more harmonized regulatory frameworks would provide greater clarity and predictability for investors. Establishing regional standards for crypto regulation, similar to the EU’s MiCAR, could help create a more cohesive and attractive investment environment.
- Countries in the Americas could adopt more competitive tax policies to attract crypto investors. This could include tax incentives for long-term holding of cryptocurrencies, reduced capital gains taxes, or exemptions for specific crypto-related activities like staking or mining. Such measures would make the region more appealing to both domestic and international investors.
- As the crypto space continues to evolve, clear regulatory guidelines are needed for new and emerging technologies such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and stablecoins. By providing legal certainty in these areas, countries in the Americas can foster innovation while ensuring investor protection.
- Public-private partnerships can help ensure that regulations are well-informed, practical, and supportive of industry growth, while also addressing concerns related to financial stability and consumer protection.
- Improving the understanding of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology among regulators, lawmakers, and the general public is crucial. Governments could invest in educational initiatives to increase awareness and knowledge about the benefits and risks of cryptocurrencies. This could lead to more informed policymaking and greater public trust in digital assets.
Asia
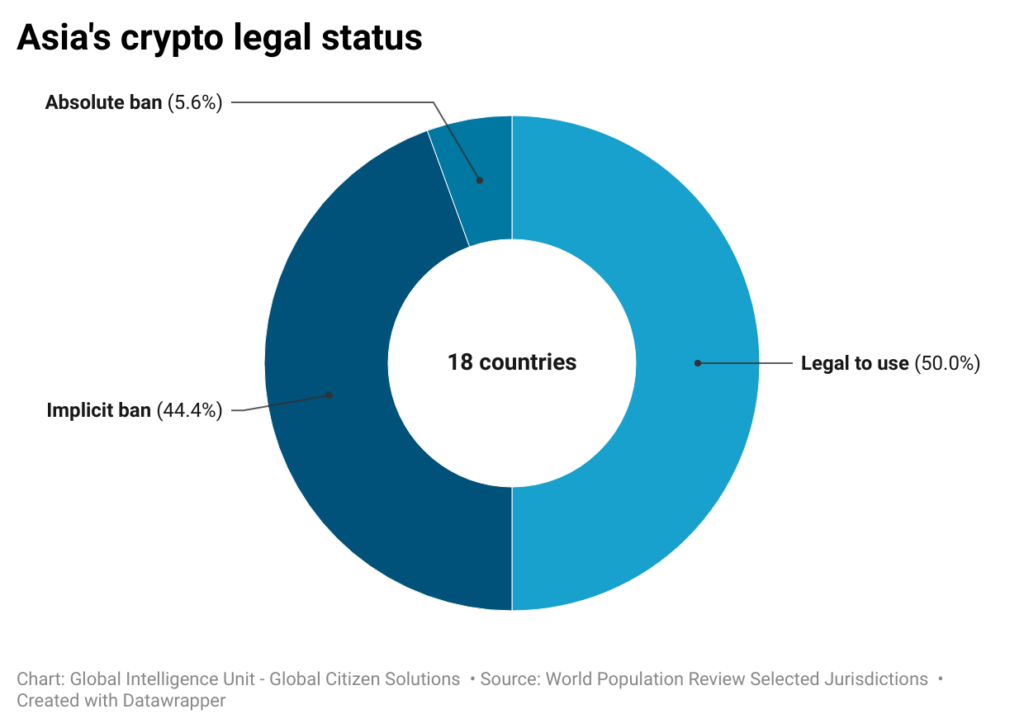
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies in Asia is highly diverse, reflecting varying levels of acceptance and regulatory rigor across different countries. Overall, 9 out of 18 (50%) jurisdictions researched in Asia have imposed some kind of a ban or significant difficulties for cryptocurrency mining and exchanges (chart below). Apart from concerns related to AML /CTF, and KYC regulations, energy consumption and lack of technological infrastructure are significant factors contributing to the curbing of cryptocurrency markets in Asia.39Lee, D. K. C., Shih, C. M., & Zheng, J. (2023). Asian CBDCs on the rise: An in-depth analysis of developments and implications. Quantitative Finance and Economics, 7(4), 665-696. https://doi.org/10.3934/QFE.2023032
Japan and South Korea lead the region with comprehensive regulatory frameworks that emphasize investor protection and market integrity. In Japan, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) strictly regulates crypto exchanges, enforcing compliance with AML and CFT measures.40Anderson Mori & Tomotsune. (2023). Blockchain & Cryptocurrency Regulation 2024: Japan Chapter. Mondaq. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from https://www.mondaq.com/fin-tech/1386476/blockchain–cryptocurrency-regulation-2024-japan-chapter South Korea, on the other hand, is on the cusp of implementing the Digital Asset Basic Act (DABA), which will regulate the entire crypto industry, including NFTs and ICOs.41Cointelegraph. (2022, May 12). Leaked report: South Korea to establish crypto framework by 2024. Retrieved from https://cointelegraph.com/news/leaked-report-south-korea-to-establish-crypto-framework-by-2024 The South Korean government is also exploring a central bank digital currency (CBDC) to further integrate digital assets into the financial system.
Japan and South Korea both have developed comprehensive tax frameworks for cryptocurrencies, reflecting their cautious yet structured approach to this emerging financial technology. In Japan, income from activities such as cryptocurrency mining, trading, and exchanges is categorized as “miscellaneous income” and is subject to progressive income tax rates, which can range from 5% to 45%, depending on the individual’s total income. Japan also taxes cryptocurrency gains when they are exchanged for other cryptocurrencies or converted to fiat currency. However, since 2017, Japan has exempted cryptocurrency transactions from its consumption tax, making it somewhat more favorable for crypto users in that specific regard.
South Korea, on the other hand, categorizes income from cryptocurrency mining as “business income” if it meets certain thresholds, and applies standard income tax rates that can reach up to 42%. For cryptocurrency trading, South Korea imposes a capital gains tax of 20% on profits exceeding 2.5 million KRW (approximately $2,000) per year. This tax applies to both residents and non-residents. South Korea’s approach is more stringent in terms of monitoring and reporting, with requirements for exchanges to report transactions above a certain threshold to tax authorities. In comparison, while both countries impose significant tax burdens on cryptocurrency activities, South Korea’s framework is more detailed and includes lower thresholds for tax exemptions, making it slightly less favorable than Japan’s for crypto investors and traders.
In contrast, countries like Vietnam (7th in public adoption rates) and Indonesia (4th in public adoption rates) are still in the process of developing their regulatory frameworks. Vietnam, while not having outright banned cryptocurrencies, emphasizes the need for a robust legal structure to mitigate risks such as money laundering. The Ministry of Justice is actively working on regulatory proposals to align with international AML standards, aiming to improve the country’s standing with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).42Cryptonews. (2024, June 6). Vietnam not banning crypto, legal framework needed: Ministry. Retrieved from https://cryptonews.com/news/vietnam-not-banning-crypto-legal-framework-needed.htm Indonesia does not allow cryptocurrencies as payment methods making it implicitly banned. The Commodity Futures Trading Regulatory Agency (Bappebti) oversees crypto exchanges43Cointelegraph. (2022, May 12). Leaked report: South Korea to establish crypto framework by 2024. Retrieved from https://cointelegraph.com/news/leaked-report-south-korea-to-establish-crypto-framework-by-2024, focusing on consumer protection, KYC rules, and preventing the misuse of cryptocurrencies for illegal activities by implementing AML/CTR legislation.
India’s regulatory landscape is complex, with significant concerns from both the government and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regarding cryptocurrencies’ potential impact on financial stability. Currently, cryptocurrencies are not considered legal tender in India, meaning they cannot be used for everyday purchases or official transactions. However, individuals and entities can hold, trade, and invest in digital assets. The legal ambiguity is compounded by a proposed bill that, if passed, could ban private cryptocurrencies entirely, adding to the uncertainty in the market. Despite these concerns, India is preparing comprehensive regulations to balance innovation with investor protection and financial integrity.44Global Legal Insights. (n.d.). India: Blockchain & cryptocurrency regulation 2024. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from https://www.globallegalinsights.com/practice-areas/blockchain-laws-and-regulations/india
With over 117 million crypto users as of 2024, India ranks among the top countries in terms of crypto adoption. This surge is fueled by a young, tech-savvy population eager to explore alternative investment opportunities in a fast-growing digital economy. Cryptocurrencies have captured the imagination of Indian investors, particularly millennials and Gen Z, who are looking for high returns and diversification beyond traditional asset classes like stocks, gold, and real estate.
However, the regulatory environment in India has been complex and somewhat hostile towards cryptocurrencies. The Indian government has oscillated between banning cryptocurrencies and regulating them, creating a sense of uncertainty in the market. In 2022, the government imposed a 30% tax on income from cryptocurrency transactions, making it one of the highest tax rates on crypto globally. Additionally, a 1% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on all crypto transactions exceeding a certain threshold was introduced, adding to the burden on traders and investors.
Despite regulatory challenges, India’s technological infrastructure for cryptocurrencies is improving. The country has seen the rise of several homegrown crypto exchanges, such as WazirX and CoinDCX, which provide users with easy access to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. These platforms have invested heavily in user education, security, and customer service to build trust in the market. Furthermore, the adoption of blockchain technology in various sectors, including finance, supply chain, and governance, has bolstered the legitimacy of cryptocurrencies and related technologies in India. However, the full potential of this market remains constrained by regulatory uncertainty and the risk of further government crackdowns.
The sentiment among Indian crypto investors is a mix of optimism and caution. On one hand, the massive returns on investments seen in the early years of crypto have driven widespread interest, especially among younger investors. On the other hand, the high tax rates and regulatory ambiguity have led some investors to consider diversifying their portfolios or even exiting the market. Additionally, the lack of legal protection for crypto assets and the potential for future bans or restrictions have made many investors wary. Nevertheless, the potential for growth remains strong, especially if the government moves towards clearer and more supportive regulation.
Given the high tax burden and regulatory uncertainty in India, many crypto investors may consider relocating to more crypto-friendly jurisdictions to optimize their tax liabilities and operate in a stable regulatory environment. The UAE, particularly Dubai, is a top choice due to its zero personal income tax, no capital gains tax, and supportive regulatory environment. Other attractive destinations include Singapore, with its robust financial sector and no capital gains tax; Portugal, known for its tax-friendly policies; Switzerland’s “Crypto Valley” offering low taxes and strong financial privacy; and Malta, with its clear regulatory framework and attractive tax incentives for crypto investors.
Pakistan, on the other hand, represents a more cautious approach towards cryptocurrency regulation. The State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) currently prohibits the use of digital currencies,45State Bank of Pakistan. (2018). Prohibition of dealing in virtual currencies/tokens. Retrieved from https://www.sbp.org.pk/warnings/pdf/2018/PBNT-VC.pdf denotating that Pakistani government shows a hardened stance towards cryptocurrencies. Recent reports46Mahmood, A. (2023). Issues of legislation of cryptocurrency in Pakistan: An analysis. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/378952790_Issues_of_Legislation_of_Cryptocurrency_in_Pakistan_An_Analysis indicate that the authorities are planning to introduce a complete ban on cryptocurrency usage in the near future, emphasizing the risks associated with these digital assets. This potential ban reflects concerns over fraud, money laundering, and other illegal activities that can be facilitated by cryptocurrencies.
Despite stringent regulations, there is a strong desire among Chinese citizens to invest in cryptocurrency.47ThinkChina. (n.d.). Rising cryptocurrency appeal in China despite ban and escalating restrictions. Retrieved from https://www.thinkchina.sg/economy/rising-cryptocurrency-appeal-china-despite-ban-and-escalating-restrictions The rapid growth and high volatility of cryptocurrencies offer opportunities for substantial gains, which is particularly appealing in a country where traditional investment avenues are often limited by government controls.48U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission. (2021). Chinese government’s evolving control of the nonstate sector. Retrieved from https://www.uscc.gov/sites/default/files/2021-11/Chapter_2_Section_3–Chinese_Governments_Evolving_Control_of_the_Nonstate_Sector.pdf However, the regulatory landscape in China presents significant barriers to these aspirations,49IFC Review. (2024, January 31). China to stiffen crypto regulations with new anti-money laundering laws. Retrieved from https://www.ifcreview.com/news/2024/january/china-china-to-stiffen-crypto-regulations-with-new-anti-money-laundering-laws/ prompting individuals to seek alternative methods to participate in the crypto market.
One viable option for Chinese miners and investors is to relocate to countries with more favorable cryptocurrency regulations. Nations such as the United States, Switzerland, Singapore, the UAE, Germany, Japan, and specially Hong Kong, offer robust legal frameworks that support cryptocurrency activities. These destinations, often referred to as havens for Chinese “bitcoin refugees”,50BBC News. (2021, September 2). Texas abortion: US Supreme Court votes to uphold new law. Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-58414555 have established themselves as global financial hubs with progressive stances on digital assets. They provide a secure environment for crypto investors and miners, particularly those looking for new locations for their mining and exchange operations.
In fact, in recent years, there has been a significant influx of migrants from mainland China to Hong Kong, particularly under the Top Talent Pass Scheme, which was introduced in late 2022. By 2023, about 37,000 applications from mainland Chinese had been approved under this scheme.51Leung, K. (2023, November). Chinese arrivals fill gaps left by Hong Kong exodus. The Diplomat. https://thediplomat.com/2023/11/chinese-arrivals-fill-gaps-left-by-hong-kong-exodus/ This migration trend is part of a broader pattern where mainland Chinese professionals and families are moving to Hong Kong for better career opportunities, educational prospects for their children, and the relatively greater freedoms available compared to mainland China. Hong Kong has indeed become an attractive destination for Chinese crypto refugees. This interest is largely driven by Hong Kong’s relatively open financial system and regulatory environment compared to mainland China, where stringent restrictions and crackdowns on cryptocurrency activities have been enforced.
The UAE, particularly Dubai, is also appealing for Chinese crypto investors, the country offers zero personal income tax, no capital gains tax, and supportive regulations, making it a global hub for cryptocurrencies. Switzerland, especially the Crypto Valley in Zug, provides low taxes on crypto assets and strong legal protection, known for its financial privacy and stability. Portugal is another favorable destination, offering no capital gains tax on individual crypto earnings and a stable, supportive regulatory environment.
Taiwan also presents a potentially attractive option, offering no specific tax on crypto investments and a generally supportive legal framework. Although Taiwan’s regulatory environment is still evolving, it provides a relatively secure setting for crypto investors, with political stability and advanced infrastructure. Taiwan’s proximity and cultural ties to China may appeal to investors seeking a balance between familiarity and a more open regulatory environment.
For those who choose to remain in China, investing in cryptocurrencies involves navigating a complex and risky landscape. Engaging in crypto activities from within China typically requires the use of VPNs to access foreign exchanges and services, which is illegal and can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. Additionally, Chinese authorities are increasingly vigilant in monitoring and cracking down on illegal crypto transactions,52ReadWrite. (2023, June 6). Chinese authorities shut down illegal crypto service. Retrieved from https://readwrite.com/chinese-authorities-shut-down-illegal-crypto-service/ making it more difficult and dangerous to engage in such activities. The use of unregulated or less-secure platforms exposes investors to significant cybersecurity threats and the potential for fraud. The lack of legal protection and the high risk of asset loss make this approach highly precarious.
Regional Considerations
- Singapore remains one of the most attractive destinations for crypto investors in Asia ans worldwide due to its robust financial infrastructure, clear regulations, and favorable tax policies, including no capital gains tax. Singapore’s supportive stance towards digital assets and its well-established regulatory environment make it a prime location for both individual and institutional investors looking for stability and growth potential.
- Both Japan and South Korea offer comprehensive and well-structured regulatory frameworks that provide significant investor protection and market integrity. Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA) and South Korea’s upcoming Digital Asset Basic Act (DABA) ensure that the crypto markets operate under clear, transparent rules. These countries are ideal for investors seeking a stable and predictable environment, although they should be prepared for substantial tax obligations.
- The UAE, particularly Dubai, offers zero personal income tax, no capital gains tax, and a supportive regulatory environment, making it a highly attractive destination for crypto investors. This is especially appealing for investors from countries with higher tax burdens, such as India, who are seeking to optimize their tax liabilities in a more favorable jurisdiction.
- While India’s regulatory environment is currently complex and somewhat hostile towards cryptocurrencies, with high tax rates and potential bans on the horizon, the country’s large, tech-savvy population and growing crypto adoption present significant opportunities. Investors should stay informed about ongoing regulatory changes and be prepared to adapt their strategies accordingly and even consider international relocation.
- Investors should exercise caution in countries like Vietnam, Indonesia, and Pakistan, where regulatory frameworks are either underdeveloped or hostile towards cryptocurrencies. The risks associated with regulatory crackdowns, potential bans, and legal ambiguities in these countries outweigh the potential benefits, making them less attractive for crypto investments.
Recommendations
- Given the diverse regulatory approaches across Asia, a more harmonized framework could help create a consistent and predictable environment for crypto investors. Establishing regional standards or guidelines, possibly through organizations like the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) or the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), could reduce regulatory uncertainty and encourage cross-border investment.
- Especially in countries like China, India, and Vietnam, where public adoption of cryptocurrencies is high, shifting towards a more nuanced regulatory approach—rather than imposing blanket bans or excessively punitive taxes—would benefit both investors and the nations themselves. By adopting balanced regulations, these countries could retain their crypto investors and prevent them from relocating to more favorable jurisdictions, thereby fostering local innovation and economic growth.
- Some Asian countries face challenges related to inadequate technological infrastructure, which can hinder the growth of the crypto industry. Investing in the development of blockchain technology, enhancing internet connectivity, and supporting digital education initiatives would provide a stronger foundation for the crypto economy, making the region more attractive to investors.
Africa
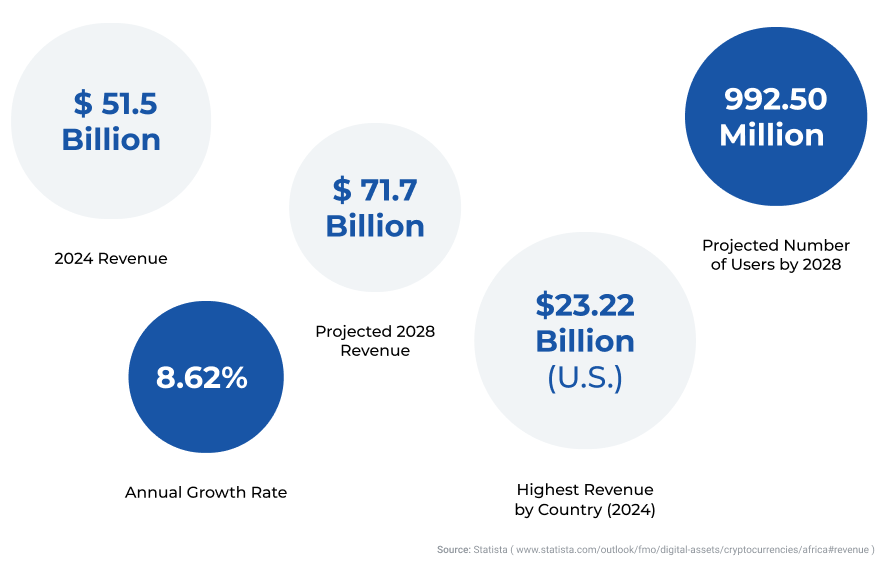
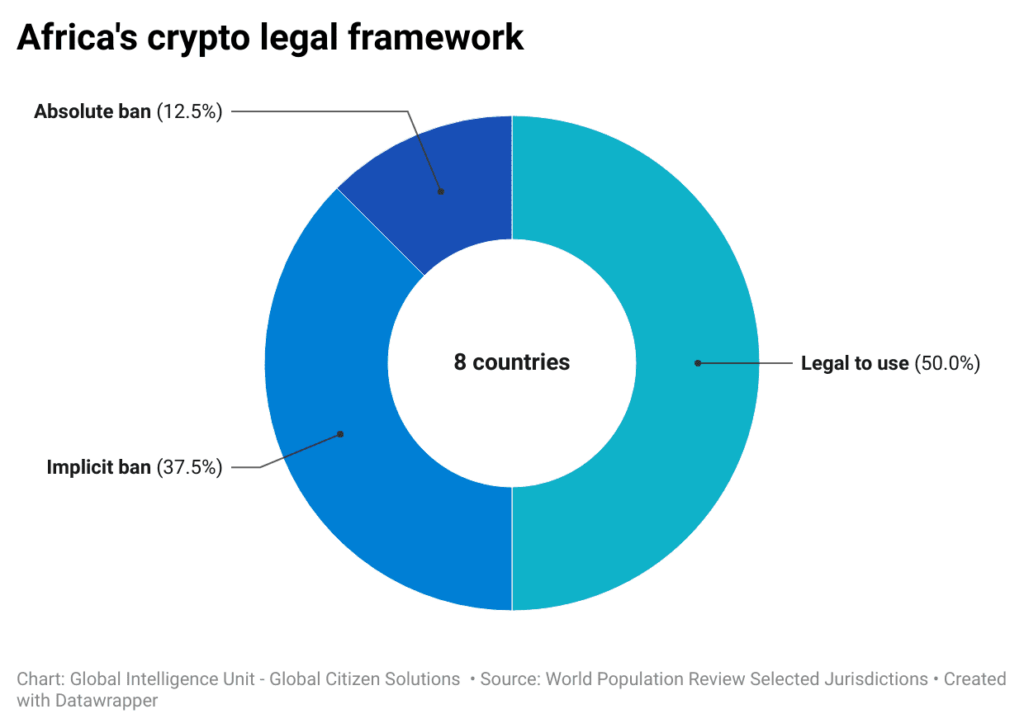
The cryptocurrency market in Africa is experiencing significant growth despite facing various regulatory and infrastructural challenges. Many African countries have been skeptical about cryptocurrencies due to concerns over financial stability, consumer protection, and potential misuse for illicit activities. 50% out of 8 countries, have either imposed a total or implicit ban on cryptocurrencies (see chart below). Despite these regulatory challenges, the adoption of cryptocurrencies in Africa is driven by factors such as financial inclusion, widespread public adoption in some countries, the need for efficient remittance systems, and the entrepreneurial spirit among the youth.
According to previously mentioned data, Millennials and Gen Z are more inclined to invest in cryptocurrencies, positioning the continent as a rapidly growing market for digital assets. Africa, the second most populated continent with an estimated 1.495 billion people, has the youngest population globally, with a median age of 19.4 years. Approximately 60% of its population is under the age of 25.53StatisticsTimes. (2024). Africa population 2024. Retrieved from https://statisticstimes.com/demographics/africa-population.php As this youthful demographic increasingly engages with digital technologies, the continent is poised to become a significant player in the global cryptocurrency landscape, provided that regulatory frameworks evolve to support this growth responsibly.
In this sense, Kenya stands out as the largest cryptocurrency market in East Africa, boasting the highest transaction volumes and user interest in the region.54Freeman Law. (n.d.). Kenya and cryptocurrency: Laws and regulations. Retrieved from https://freemanlaw.com/cryptocurrency/kenya/ It is one of the top five cryptocurrency markets on the continent55Digital Observer 4 Africa. (n.d.). Cryptocurrency adoption in Africa. Do4Africa. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.do4africa.org/en/cryptocurrency-adoption-in-africa/, with cryptocurrencies being used beyond investment purposes. Notably, crypto payments have been integrated into e-commerce and remittance services, enhancing financial transactions and offering alternative payment solutions.56International Monetary Fund. (2024). Article title. IMF eLibrary. Retrieved from https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/journals/063/2024/001/article-A001-en.xml
The regulatory landscape in Kenya is evolving from a previously negative stance to a more welcoming approach. In 2023, significant discussions in the parliament focused on cryptocurrency regulations and major projects. The Kenyan cryptocurrency community has opposed the Capital Markets (Amendment) Bill 202357Umoja Protocol. (2023). The state of crypto regulation: Kenya. Medium. Retrieved from https://medium.com/umoja-protocol/the-state-of-crypto-regulation-kenya-8a11189bda6b, which seeks to classify crypto assets as securities and impose a capital gains tax. In response, the Blockchain Association of Kenya (BAK) filed a complaint against the bill with the High Court. Progress has been made as the National Assembly’s Departmental Committee on Finance and National Planning has directed BAK to draft a preliminary bill to regulate virtual asset service providers58Techpoint Africa. (2024, February 7). Kenyan lobby group takes the country’s first-ever crypto bill to parliament. Techpoint Africa. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://techpoint.africa/2024/02/07/blockchain-group-drafts-kenya-crypto-bill/, positioning Kenya at the forefront of regulatory innovation led by industry representatives.
In South Africa, cryptocurrencies are considered legal and subject to tax regulations59South African Revenue Service. (n.d.). Crypto assets & tax. South African Revenue Service. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.sars.gov.za/individuals/crypto-assets-tax/#:~=Yes%2C%20normal%20income%20tax%20rules,it%20is%20received%20or%20accrued. The South African Reserve Bank oversees the industry60South African Reserve Bank. (n.d.). Fintech. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.resbank.co.za/en/home/quick-links/fintech, classifying digital currencies as financial products.
The Central African Republic took a groundbreaking step by making Bitcoin an official legal tender in 2022.61Sango. (n.d.). Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://sango.org This move positioned the country alongside El Salvador as one of the few nations globally to adopt Bitcoin as a national currency. However, this decision faced challenges, including opposition from the regional central bank, leading to a repeal of the law in 2023.62Fuje, H., Quayyum, S., & Molosiwa, T. (2022, November 22). Africa’s growing crypto market needs better regulations. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.imf.org/en/Blogs/Articles/2022/11/22/africas-growing-crypto-market-needs-better-regulations
Several African countries have imposed implicit bans on cryptocurrencies. In these nations, while there is no explicit prohibition, significant restrictions exist that limit their use. Nigeria is a prime example, where the Central Bank of Nigeria prohibited financial institutions from facilitating cryptocurrency transactions.63Clynch, H. (2024, January 16). ‘Resistance is futile’: Why Nigeria rolled back crypto restrictions. African Business. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://african.business/2024/01/finance-services/resistance-is-futile-why-nigeria-rolled-back-crypto-restrictions Despite this, Nigeria remains a leader in cryptocurrency adoption, driven by peer-to-peer trading and a large tech-savvy population.64EY. (2020). Fintech Nigeria Census 2020. Ernst & Young. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://assets.ey.com/content/dam/ey-sites/ey-com/en_ng/ey-fintech-nigeria-census-final.pdf
Other countries have taken a hardline stance by imposing absolute bans on cryptocurrencies. Algeria and Morocco have completely outlawed the use of digital currencies, citing concerns over financial stability, fraud, and potential misuse for illicit activities.65Techopedia. (2024, May 10). Cryptocurrency bans explained: Which countries have restricted crypto? Techopedia. https://www.techopedia.com/cryptocurrency-bans-explained-which-countries-have-restricted-crypto These countries have issued public warnings and imposed strict penalties for violations, aiming to protect their financial systems from the perceived risks associated with cryptocurrencies.
Africa is poised for remarkable economic growth, with projections indicating that eleven of the world’s twenty fastest-growing economies in 2024 will be African nations66African Development Bank. (2024, January 18). Africa dominates list of world’s 20 fastest-growing economies, 2024 African Development Bank says – Macroeconomic Report. African Development Bank Group. https://www.afdb.org/en/news-and-events/press-releases/africa-dominates-list-worlds-20-fastest-growing-economies-2024-african-development-bank-says-macroeconomic-report-68751, according to the African Development Bank Group. The continent’s real GDP growth is expected to average 3.8% in 2024 and 4.2% in 2025, outpacing the global averages of 2.9% and 3.2%, respectively. This robust economic outlook is further complemented by a demographic advantage, as the youthful populations of Millennials and Gen Zs are more inclined to invest in cryptocurrencies (see above).
Such a trend is expected to drive the expansion of the crypto market, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and in key economies such as Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa. These countries are leveraging digital currencies to enhance financial inclusion and streamline the remittance market, providing efficient and cost-effective solutions for cross-border transactions. As regulatory frameworks evolve to better support and integrate cryptocurrencies, the development of a strong regulatory framework in Africa can significantly benefit market growth, ensuring a secure and sustainable environment for digital financial innovations. This evolution will strengthen Africa’s position in the global digital economy, supported by its innovative financial practices and dynamic youth.
Regional Considerations
- Africa’s young and tech-savvy population, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, is driving significant growth in the cryptocurrency market. With 60% of the continent’s population under the age of 25, Africa is well-positioned to become a major player in the global cryptocurrency landscape. As these younger generations increasingly adopt digital technologies, the continent’s crypto market could expand rapidly, provided that regulatory frameworks evolve to support this growth responsibly.
- While several African countries have imposed bans or restrictions on cryptocurrencies, others like Kenya and South Africa are moving towards more balanced regulatory frameworks. By developing clear, supportive regulations that protect consumers while fostering innovation, African countries can harness the benefits of cryptocurrencies to enhance financial inclusion, streamline remittances, and support economic growth, particularly in rapidly developing regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa.
- The varying approaches to cryptocurrency regulation across Africa reflect both challenges and opportunities. Countries like Nigeria, despite implicit bans, continue to see high levels of adoption through peer-to-peer trading, demonstrating the strong demand for digital assets. On the other hand, Kenya’s evolving regulatory landscape, with industry-driven initiatives, highlights the potential for Africa to lead in regulatory innovation, setting examples for other regions.
- Africa’s robust economic growth projections, with several of the world’s fastest-growing economies in 2024, create a fertile ground for the expansion of the cryptocurrency market. As the continent’s economies continue to grow, particularly in key markets like Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa, the integration of digital currencies into financial systems can further accelerate economic development, provided that supportive regulatory frameworks are in place to ensure security and sustainability.
Recommendations
- Countries should establish transparent and consistent regulations for cryptocurrencies that protect investors while encouraging innovation. This includes defining the legal status of cryptocurrencies, setting up licensing requirements for crypto businesses, and establishing clear guidelines for taxation. By providing a stable regulatory environment, countries can attract both domestic and international crypto investors.
- African countries can leverage cryptocurrencies to enhance financial inclusion, especially in regions where traditional banking services are limited. By supporting crypto-based solutions for remittances, payments, and microfinance, governments can attract investors interested in social impact while also addressing local financial needs.
- To make their markets more attractive, countries could offer tax incentives such as reduced capital gains taxes or tax exemptions for long-term holdings of cryptocurrencies. Simplifying compliance requirements for crypto businesses and investors can also make the investment environment more appealing, reducing the administrative burden and costs associated with regulatory adherence.
- Governments should invest in the necessary technological infrastructure to support blockchain and cryptocurrency activities. This includes improving internet access, cybersecurity measures, and digital literacy. Additionally, promoting blockchain education and skills training can build a knowledgeable workforce, making the country more attractive to crypto businesses and investors looking to establish operations.
- By encouraging collaboration between the government, financial institutions, and the private sector, African countries can create a more dynamic and supportive environment for crypto investments. Public-private partnerships can drive innovation, develop tailored solutions to local challenges, and ensure that regulations are informed by industry insights.
Oceania
In Oceania, the adoption of cryptocurrencies has been steadily growing. Countries in this region, particularly Australia and New Zealand, have shown a significant interest in digital currencies. The awareness and usage of cryptocurrencies in Oceania reflect a global trend towards embracing new financial technologies, albeit with regional nuances.
Australia stands out as a leader in the adoption and regulation of cryptocurrencies in Oceania. The Australian government has been proactive in creating a regulatory framework that fosters innovation while protecting consumers. The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) regulates cryptocurrency exchanges and requires them to register and comply AML/CTR and KYC laws.67Australian Government Treasury. (2023). Regulating digital asset platforms. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://treasury.gov.au/consultation/c2023-427004
Major cryptocurrency exchanges such as CoinSpot, BTC Markets, and Independent Reserve operate in Australia68Doe, J. (2023, June 8). How to buy cryptocurrency. Forbes Advisor Australia. https://www.forbes.com/advisor/au/investing/cryptocurrency/how-to-buy-cryptocurrency/, providing a robust infrastructure for trading and investing in digital currencies. The country has seen a surge in both public and institutional adoption, with businesses increasingly accepting cryptocurrencies as a form of payment.69Nasdaq. (2022, August 18). Over 400 Australian retailers now accept Bitcoin as payment. Nasdaq. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/over-400-australian-retailers-now-accept-bitcoin-as-payment
New Zealand has also embraced cryptocurrencies, albeit with a more cautious approach compared to Australia. The Financial Markets Authority (FMA) oversees cryptocurrency activities, ensuring compliance with financial regulations such as AML/CTR and KYC laws.70Financial Markets Authority. (n.d.). Cryptocurrencies. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.fma.govt.nz/business/services/cryptocurrencies/
Popular exchanges like Easy Crypto and BitPrime cater to the local market, and the country has witnessed growing interest from both individuals and businesses.71 Statista. (n.d.). Cryptocurrencies – New Zealand. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/outlook/fmo/digital-assets/cryptocurrencies/new-zealand The government’s open stance towards innovation in the financial sector has encouraged the growth of cryptocurrency
In smaller island nations such as Fiji, Samoa, and Tonga, the adoption of cryptocurrencies is still in its nascent stages. These countries have shown interest in the potential of digital currencies to enhance financial inclusion and improve access to financial services.72International Monetary Fund. (2024). Cryptocurrencies: Trends, risks, and adoption. IMF eLibrary. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/journals/087/2024/003/article-A001-en.xml Specific initiatives and pilot projects are being explored, though widespread adoption is yet to be realized.
The regions of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia exhibit varied trends in cryptocurrency adoption.73Chainalysis. (n.d.). Central & Southern Asia cryptocurrency adoption. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/central-southern-asia-cryptocurrency-adoption/ While some areas are exploring the use of digital currencies for remittances and cross-border transactions, challenges such as lack of infrastructure and regulatory clarity hinder broader adoption. However, these regions present significant opportunities for growth, particularly in enhancing financial inclusion and economic development.
Regional considerations
- Australia is at the forefront of cryptocurrency adoption and regulation in Oceania. The country has developed a robust regulatory framework, overseen by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), which fosters innovation while ensuring consumer protection. This proactive approach has led to a surge in both public and institutional adoption, with major exchanges operating within the country and businesses increasingly accepting cryptocurrencies as payment.
- New Zealand is also embracing cryptocurrencies, though with a more cautious regulatory approach compared to Australia. The Financial Markets Authority (FMA) ensures compliance with financial regulations, contributing to a growing interest in digital currencies among both individuals and businesses. The government’s openness to financial innovation has encouraged the expansion of cryptocurrency activities, supported by popular local exchanges like Easy Crypto and BitPrime.
- In smaller Pacific island nations such as Fiji, Samoa, and Tonga, cryptocurrency adoption is still in its early stages. While these countries are exploring the potential of digital currencies to improve financial inclusion and access to services, challenges like infrastructure limitations and regulatory uncertainty are significant barriers. However, these regions present opportunities for growth, particularly in utilizing cryptocurrencies for remittances and economic development in areas with limited financial infrastructure.
Recommendations
- Countries in Oceania, particularly Australia and New Zealand, should continue to develop and refine their regulatory frameworks to provide clarity and confidence to investors. Ensuring that regulations are consistent across the region would help create a unified market that attracts both domestic and international crypto investors. Simplifying compliance processes and providing clear guidelines for new and emerging crypto technologies, such as DeFi and NFTs, would further encourage investment.
- Smaller island nations like Fiji, Samoa, and Tonga have the opportunity to leverage cryptocurrencies to enhance financial inclusion and improve access to financial services.
- For regions like Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia, where infrastructure challenges and regulatory uncertainties exist, investing in digital infrastructure and improving internet connectivity are crucial. Additionally, promoting digital literacy and education around cryptocurrencies can help build a knowledgeable population that is capable of participating in the digital economy, making the region more attractive to investors.
- Australia can continue to position itself as a regional hub for cryptocurrency innovation by offering tax incentives for crypto businesses, supporting blockchain research and development, and fostering public-private partnerships.
Conclusion
The Global Cryptocurrency Report by Global Citizen Solutions provides a detailed and insightful analysis of the global landscape for cryptocurrency investment and adoption. This extensive study, which researched 75 jurisdictions across 13 key indicators subdivided into five sub-indexes—Regulatory Landscape, Economic Environment (including favorable tax regimes), Attractiveness and Public Adoption, Tech and Innovation, and Green Transition and Governance—highlights significant regional differences and most friendly jurisdictions for crypto investment. The report further highlights that 76% of the assessed countries permit crypto investing, though 23% have imposed bans, affecting a significant portion of High-Net-Worth Individuals globally.
Europe emerges as a leading hub for crypto-friendly policies, with countries like Switzerland and Liechtenstein offering highly favorable tax regimes that exempt cryptocurrency gains, positioning them as attractive destinations for crypto investors. The report also recognizes Asia and the Middle East, particularly Singapore and the UAE, where 0% crypto taxes and strong support for blockchain innovation contribute to their high rankings.
In addition to Europe and Asia, Latin America is making considerable progress in becoming more crypto-friendly. Brazil, Chile and El Salvador, in particular, are leading the charge with improved legislation, increased exchange availability, and infrastructure development. Brazil’s position as the sixth-largest country for crypto investors and El Salvador’s pioneering move to make Bitcoin legal tender demonstrate the region’s growing significance in the global crypto ecosystem.
The correlation between crypto-friendly environments and relocation as a strategy to secure more appealing markets is another key conclusion of the report. High cryptocurrency adoption rates in a country do not necessarily equate to a crypto-friendly environment, as strict regulations and uncertain legal frameworks can still pose significant challenges for investors. This disparity often leads investors to consider international relocation to invest in more favorable and stable crypto environments. A notable example is the phenomenon of “crypto refugees” from China, who have sought refuge in Hong Kong due to China’s stringent crackdown on cryptocurrency activities. Similarly, Indian nationals, facing a lack of clear regulatory frameworks and potential restrictions in India, are increasingly looking towards more welcoming jurisdictions like Singapore and the UAE. This alignment underscores the growing importance of cryptocurrency in national policies and its potential as a tool for attracting investment.
Furthermore, cryptocurrency investment is increasingly seen as a generational phenomenon, with the majority of investors belonging to Millennials and Gen Z. These generations are particularly inclined towards principled investments, prioritizing ethical considerations such as sustainability. This is especially relevant in the context of cryptocurrency, which is known for its high energy consumption. Recognizing this, the report underscores the importance of green transition in crypto-friendly environments, emphasizing the strong connection between progressive crypto policies and green energy initiatives. Notably, 13 of the top 20 countries identified in the report also rank highly in renewable energy progress, reflecting a growing alignment between sustainability and cryptocurrency investment. This focus on green energy is crucial for attracting younger investors who are committed to making environmentally responsible financial decisions.
Overall, the Global Cryptocurrency Report offers a valuable blueprint for countries seeking to attract crypto investors by emphasizing the need for sensible regulations, sustainability, and innovation. By identifying the most progressive and advantageous environments for crypto investment, the report provides investors, policymakers, and stakeholders with critical insights to navigate the evolving cryptocurrency landscape. As the demand for ethical and sustainable investment options grows, this report serves as a guide to the regions leading the way in integrating cryptocurrency into their economies.

